Mutually exclusive splicing of the insect Dscam pre-mRNA directed by competing intronic RNA secondary structures
- PMID: 16213213
- PMCID: PMC2366815
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.07.028
Mutually exclusive splicing of the insect Dscam pre-mRNA directed by competing intronic RNA secondary structures
Abstract
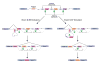
Drosophila Dscam encodes 38,016 distinct axon guidance receptors through the mutually exclusive alternative splicing of 95 variable exons. Importantly, known mechanisms that ensure the mutually exclusive splicing of pairs of exons cannot explain this phenomenon in Dscam. I have identified two classes of conserved elements in the Dscam exon 6 cluster, which contains 48 alternative exons--the docking site, located in the intron downstream of constitutive exon 5, and the selector sequences, which are located upstream of each exon 6 variant. Strikingly, each selector sequence is complementary to a portion of the docking site, and this pairing juxtaposes one, and only one, alternative exon to the upstream constitutive exon. The mutually exclusive nature of the docking site:selector sequence interactions suggests that the formation of these competing RNA structures is a central component of the mechanism guaranteeing that only one exon 6 variant is included in each Dscam mRNA.
Figures






Comment in
-
Alternative splicing--when two's a crowd.Cell. 2005 Oct 7;123(1):1-3. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.010. Cell. 2005. PMID: 16213205
References
-
- Black DL. Protein diversity from alternative splicing: A challenge for bioinformatics and post-genome biology. Cell. 2000;103:367–370. - PubMed
-
- Graveley BR. Alternative splicing: increasing diversity in the proteomic world. Trends Genet. 2001;17:100–107. - PubMed
-
- Johnson JM, Castle J, Garrett-Engele P, Kan Z, Loerch PM, Armour CD, Santos R, Schadt EE, Stoughton R, Shoemaker DD. Genome-wide survey of human alternative pre-mRNA splicing with exon junction microarrays. Science. 2003;302:2141–2144. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

