Constitutive activation of prosurvival signaling in alveolar mesenchymal cells isolated from patients with nonresolving acute respiratory distress syndrome
- PMID: 16214815
- PMCID: PMC1382273
- DOI: 10.1152/ajplung.00276.2005
Constitutive activation of prosurvival signaling in alveolar mesenchymal cells isolated from patients with nonresolving acute respiratory distress syndrome
Abstract
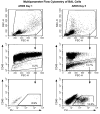
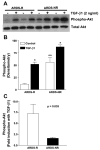
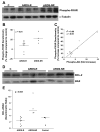
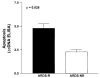
Acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is a clinical syndrome characterized by stereotypic host inflammatory and repair cellular responses; however, mechanisms regulating the resolution of ARDS are poorly understood. Here, we report the isolation and characterization of a novel population of mesenchymal cells from the alveolar space of ARDS patients via fiber-optic bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL). BAL was performed on 17 patients during the course of ARDS. Immunofluorescence staining and multiparameter flow cytometric analysis defined a population of alveolar mesenchymal cells (AMCs) that are CD45-/prolyl-4-hydroxylase+/alpha-smooth muscle actin+/-. AMCs proliferated in ex vivo cell culture for multiple passages; early passage (3-5) cells were subsequently analyzed in 13 patients. AMCs isolated from patients with persistent or nonresolving ARDS (ARDS-NR, n = 4) demonstrate enhanced constitutive activation of prosurvival signaling pathways involving PKB/Akt, FKHR, and BCL-2 family proteins compared with AMCs from patients with resolving ARDS (ARDS-R, n = 9). Exogenous transforming growth factor-beta1 markedly induces PKB/Akt activation in AMCs from ARDS-R. ARDS-NR cells are more resistant to serum deprivation-induced apoptosis compared with ARDS-R. This study identifies a novel population of mesenchymal cells that can be isolated from the alveolar spaces of ARDS patients. AMCs in patients with ARDS-NR acquire an activational profile characterized by enhanced prosurvival signaling and an antiapoptotic phenotype. These findings support the concept that apoptosis of mesenchymal cells may be an essential component of normal repair and resolution of ARDS and suggest that dysregulation of this process may contribute to persistent ARDS.
Figures


References
-
- American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society. International Multidisciplinary Consensus Classification of the Idiopathic Interstitial Pneumonias. This joint statement of the American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS) was adopted by the ATS board of directors, June 2001 and by the ERS Executive Committee, June 2001. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:277–304. - PubMed
-
- Anderson WR, Thielen K. Correlative study of adult respiratory distress syndrome by light, scanning, and transmission electron microscopy. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1992;16:615–628. - PubMed
-
- Asnaghi L, Calastretti A, Bevilacqua A, D’Agnano I, Gatti G, Canti G, Delia D, Capaccioli S, Nicolin A. Bcl-2 phosphorylation and apoptosis activated by damaged microtubules require mTOR and are regulated by Akt. Oncogene. 2004;23:5781–5791. - PubMed
-
- Bachofen M, Weibel ER. Structural alterations of lung parenchyma in the adult respiratory distress syndrome. Clin Chest Med. 1982;3:35–56. - PubMed
-
- Bernard GR, Artigas A, Brigham KL, Carlet J, Falke K, Hudson L, Lamy M, Legall JR, Morris A, Spragg R. The American-European Consensus Conference on ARDS. Definitions, mechanisms, relevant outcomes, and clinical trial coordination. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994;149:818–824. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

