Determination of RNA orientation during translocation through a biological nanopore
- PMID: 16214857
- PMCID: PMC1367018
- DOI: 10.1529/biophysj.105.068957
Determination of RNA orientation during translocation through a biological nanopore
Abstract
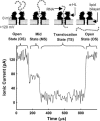
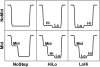
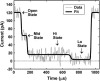
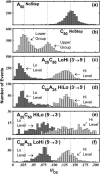
We investigate single-molecule electrophoretic translocation of A(50), C(50), A(25)C(50), and C(50)A(25) RNA molecules through the alpha-hemolysin transmembrane protein pore. We observe pronounced bilevel current blockages during translocation of A(25)C(50) and C(50)A(25) molecules. The two current levels observed during these bilevel blockages are very similar to the characteristic current levels observed during A(50) and C(50) translocation. From the temporal ordering of the two levels within the bilevel current blockages, we infer whether individual A(25)C(50) and C(50)A(25) molecules pass through the pore in a 3'-->5' or 5'-->3' orientation. Correlation between the level of current obstruction and the inferred A(25)C(50) or C(50)A(25) orientation indicates that 3'-->5' translocation of a poly C segment causes a significantly deeper current obstruction than 5'-->3' translocation. Our analysis also suggests that the 3' ends of C(50) and A(25)C(50) RNA molecules are more likely to initiate translocation than the 5' ends. Orientation dependent differences in a smaller current blockage that immediately precedes many translocation events suggest that this blockage also contains information about RNA orientation during translocation. These findings emphasize that the directionality of polynucleotide molecules is an important factor in translocation and demonstrate how structure within ionic current signals can give new insights into the translocation process.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Ionic current blockades from DNA and RNA molecules in the alpha-hemolysin nanopore.Biophys J. 2007 Nov 1;93(9):3229-40. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.107.107003. Epub 2007 Aug 3. Biophys J. 2007. PMID: 17675346 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of orientation in translocation of polymers through nanopores.J Chem Phys. 2006 Aug 28;125(8):084906. doi: 10.1063/1.2338539. J Chem Phys. 2006. PMID: 16965056
-
Microscopic Kinetics of DNA Translocation through synthetic nanopores.Biophys J. 2004 Sep;87(3):2086-97. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.104.042960. Biophys J. 2004. PMID: 15345583 Free PMC article.
-
Nanopore analytics: sensing of single molecules.Chem Soc Rev. 2009 Aug;38(8):2360-84. doi: 10.1039/b813796j. Epub 2009 Jun 15. Chem Soc Rev. 2009. PMID: 19623355 Review.
-
Biosensing with conically shaped nanopores and nanotubes.Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2006 Nov 21;8(43):4976-88. doi: 10.1039/b607360c. Epub 2006 Aug 7. Phys Chem Chem Phys. 2006. PMID: 17091150 Review.
Cited by
-
Polymer translocation through alpha-hemolysin pore with tunable polymer-pore electrostatic interaction.J Chem Phys. 2010 Jul 28;133(4):045101. doi: 10.1063/1.3464333. J Chem Phys. 2010. PMID: 20687689 Free PMC article.
-
Clustering ionic flow blockade toggles with a mixture of HMMs.BMC Bioinformatics. 2008 Aug 12;9 Suppl 9(Suppl 9):S13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-9-S9-S13. BMC Bioinformatics. 2008. PMID: 18793458 Free PMC article.
-
Slowing down single-molecule trafficking through a protein nanopore reveals intermediates for peptide translocation.Sci Rep. 2014 Jan 27;4:3885. doi: 10.1038/srep03885. Sci Rep. 2014. PMID: 24463372 Free PMC article.
-
Three decades of nanopore sequencing.Nat Biotechnol. 2016 May 6;34(5):518-24. doi: 10.1038/nbt.3423. Nat Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27153285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Controlling molecular transport through nanopores.J R Soc Interface. 2011 Oct 7;8(63):1369-78. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2011.0222. Epub 2011 Jun 29. J R Soc Interface. 2011. PMID: 21715402 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Howorka, S., S. Cheley, and H. Bayley. 2001. Sequence-specific detection of individual DNA strands using engineered nanopores. Nat. Biotechnol. 19:636–639. - PubMed
-
- Kasianowicz, J. J., S. E. Henrickson, H. H. Weetall, and B. Robertson. 2001. Simultaneous multianalyte detection with a nanometer-scale pore. Anal. Chem. 73:2268–2272. - PubMed
-
- Vercoutere, W., S. Winters-Hilt, H. Olsen, D. Deamer, D. Haussler, and M. Akeson. 2001. Rapid discrimination among individual DNA hairpin molecules at single-nucleotide resolution using an ion channel. Nat. Biotechnol. 19:248–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

