The Arabidopsis cold-responsive transcriptome and its regulation by ICE1
- PMID: 16214899
- PMCID: PMC1276035
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.105.035568
The Arabidopsis cold-responsive transcriptome and its regulation by ICE1
Abstract
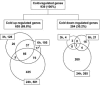
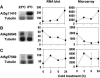
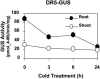
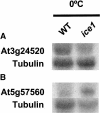
To understand the gene network controlling tolerance to cold stress, we performed an Arabidopsis thaliana genome transcript expression profile using Affymetrix GeneChips that contain approximately 24,000 genes. We statistically determined 939 cold-regulated genes with 655 upregulated and 284 downregulated. A large number of early cold-responsive genes encode transcription factors that likely control late-responsive genes, suggesting a multitude of transcriptional cascades. In addition, many genes involved in chromatin level and posttranscriptional regulation were also cold regulated, suggesting their involvement in cold-responsive gene regulation. A number of genes important for the biosynthesis or signaling of plant hormones, such as abscisic acid, gibberellic acid, and auxin, are regulated by cold stress, which is of potential importance in coordinating cold tolerance with growth and development. We compared the cold-responsive transcriptomes of the wild type and inducer of CBF expression 1 (ice1), a mutant defective in an upstream transcription factor required for chilling and freezing tolerance. The transcript levels of many cold-responsive genes were altered in the ice1 mutant not only during cold stress but also before cold treatments. Our study provides a global picture of the Arabidopsis cold-responsive transcriptome and its control by ICE1 and will be valuable for understanding gene regulation under cold stress and the molecular mechanisms of cold tolerance.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The unified ICE-CBF pathway provides a transcriptional feedback control of freezing tolerance during cold acclimation in Arabidopsis.Plant Mol Biol. 2015 Sep;89(1-2):187-201. doi: 10.1007/s11103-015-0365-3. Epub 2015 Aug 27. Plant Mol Biol. 2015. PMID: 26311645
-
Roles of the CBF2 and ZAT12 transcription factors in configuring the low temperature transcriptome of Arabidopsis.Plant J. 2005 Jan;41(2):195-211. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02288.x. Plant J. 2005. PMID: 15634197
-
Jasmonate regulates the inducer of cbf expression-C-repeat binding factor/DRE binding factor1 cascade and freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis.Plant Cell. 2013 Aug;25(8):2907-24. doi: 10.1105/tpc.113.112631. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Plant Cell. 2013. PMID: 23933884 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between cold-responsive gene regulation, metabolism and RNA processing during plant cold acclimation.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2007 Jun;10(3):290-5. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2007.04.010. Epub 2007 Apr 30. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2007. PMID: 17468037 Review.
-
CBF-dependent signaling pathway: a key responder to low temperature stress in plants.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2011 Jun;31(2):186-92. doi: 10.3109/07388551.2010.505910. Epub 2010 Oct 4. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2011. PMID: 20919819 Review.
Cited by
-
Current status for utilization of cold resistance genes and strategies in wheat breeding program.Front Genet. 2024 Oct 22;15:1473717. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1473717. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39502336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Temporal transcriptome profiling reveals expression partitioning of homeologous genes contributing to heat and drought acclimation in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.).BMC Plant Biol. 2015 Jun 20;15:152. doi: 10.1186/s12870-015-0511-8. BMC Plant Biol. 2015. PMID: 26092253 Free PMC article.
-
Cold regulation of plastid ascorbate peroxidases serves as a priming hub controlling ROS signaling in Arabidopsis thaliana.BMC Plant Biol. 2016 Jul 20;16(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0856-7. BMC Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 27439459 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Insights into the Physio-Biochemical and Molecular Mechanisms of Low Temperature Stress in Tomato.Plants (Basel). 2024 Sep 28;13(19):2715. doi: 10.3390/plants13192715. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39409585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combined Transcriptome and Metabolome Profiling Provide Insights into Cold Responses in Rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) Genotypes with Contrasting Cold-Stress Sensitivity.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 4;23(21):13546. doi: 10.3390/ijms232113546. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36362332 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Benjamini, Y., and Yekutieli, D. (2001). The control of the false discovery rate in multiple testing under dependency. Ann. Statist. 29, 1165–1188.
-
- Choi, H.I., Hong, J.H., Ha, J.O., Kang, J.Y., and Kim, S.Y. (2000). ABFs, a family of ABA-responsive element binding factors. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 1723–1730. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

