Effect of mutation of the tetratricopeptide repeat and asparatate-proline 2 domains of Sti1 on Hsp90 signaling and interaction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- PMID: 16219779
- PMCID: PMC1456168
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.105.045815
Effect of mutation of the tetratricopeptide repeat and asparatate-proline 2 domains of Sti1 on Hsp90 signaling and interaction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Abstract
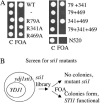
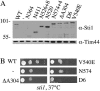
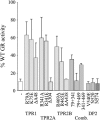
Through simultaneous interactions with Hsp70 and Hsp90 via separate tetratricopeptide repeat (TPR) domains, the cochaperone protein Hop/Sti1 has been proposed to play a critical role in the transfer of client proteins from Hsp70 to Hsp90. However, no prior mutational analysis demonstrating a critical in vivo role for the TPR domains of Sti1 has been reported. We used site-directed mutagenesis of the TPR domains combined with a genetic screen to isolate mutations that disrupt Sti1 function. A single amino acid alteration in TPR2A disrupted Hsp90 interaction in vivo but did not significantly affect function. However, deletion of a conserved residue in TPR2A or mutations in the carboxy-terminal DP2 domain completely disrupted Sti1 function. Surprisingly, mutations in TPR1, previously shown to interact with Hsp70, were not sufficient to disrupt in vivo functions unless combined with mutations in TPR2B, suggesting that TPR1 and TPR2B have redundant or overlapping in vivo functions. We further examined the genetic and physical interaction of Sti1 with a mutant form of Hsp90, providing insight into the importance of the TPR2A domain of Sti1 in regulating Hsp90 function.
Figures





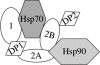
Similar articles
-
Definition of the minimal fragments of Sti1 required for dimerization, interaction with Hsp70 and Hsp90 and in vivo functions.Biochem J. 2007 May 15;404(1):159-67. doi: 10.1042/BJ20070084. Biochem J. 2007. PMID: 17300223 Free PMC article.
-
The architecture of functional modules in the Hsp90 co-chaperone Sti1/Hop.EMBO J. 2012 Mar 21;31(6):1506-17. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.472. Epub 2012 Jan 6. EMBO J. 2012. PMID: 22227520 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp90 regulates the dynamics of its cochaperone Sti1 and the transfer of Hsp70 between modules.Nat Commun. 2015 Apr 8;6:6655. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7655. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25851214 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into Sti1/Hop's cochaperone function highlight the complexity of proteostatic regulation.FEBS J. 2025 Jul;292(14):3629-3633. doi: 10.1111/febs.70108. Epub 2025 Apr 21. FEBS J. 2025. PMID: 40259657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Hsp70-Hsp90 go-between Hop/Stip1/Sti1 is a proteostatic switch and may be a drug target in cancer and neurodegeneration.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021 Dec;78(23):7257-7273. doi: 10.1007/s00018-021-03962-z. Epub 2021 Oct 22. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 34677645 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Heat shock proteins in association with heat tolerance in grasses.Int J Proteomics. 2011;2011:529648. doi: 10.1155/2011/529648. Epub 2011 Feb 24. Int J Proteomics. 2011. PMID: 22084689 Free PMC article.
-
Disrupting progression of the yeast Hsp90 folding pathway at different transition points results in client-specific maturation defects.Genetics. 2021 Mar 31;217(3):iyab009. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyab009. Genetics. 2021. PMID: 33789348 Free PMC article.
-
The co-chaperone Hch1 regulates Hsp90 function differently than its homologue Aha1 and confers sensitivity to yeast to the Hsp90 inhibitor NVP-AUY922.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e49322. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0049322. Epub 2012 Nov 14. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23166640 Free PMC article.
-
Root proteomic responses to heat stress in two Agrostis grass species contrasting in heat tolerance.J Exp Bot. 2008;59(15):4183-94. doi: 10.1093/jxb/ern258. Epub 2008 Nov 13. J Exp Bot. 2008. PMID: 19008411 Free PMC article.
-
The ribosomal biogenesis protein Utp21 interacts with Hsp90 and has differing requirements for Hsp90-associated proteins.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 19;9(3):e92569. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092569. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24647762 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abbas-Terki, T., P. A. Briand, O. Donze and D. Picard, 2002. The Hsp90 co-chaperones Cdc37 and Sti1 interact physically and genetically. Biol. Chem. 383: 1335–1342. - PubMed
-
- Carrigan, P. E., G. M. Nelson, P. J. Roberts, J. Stoffer, D. L. Riggs et al., 2004. Multiple domains of the co-chaperone Hop are important for Hsp70 binding. J Biol. Chem. 279: 16185–16193. - PubMed
-
- Carrigan, P. E., D. L. Riggs, M. Chinkers and D. F. Smith, 2005. Functional comparison of human and Drosophila Hop reveals novel role in steroid receptor maturation. J. Biol. Chem. 280: 8906–8911. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

