Regulation of LIM-kinase 1 and cofilin in thrombin-stimulated platelets
- PMID: 16219803
- PMCID: PMC1895613
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2004-11-4377
Regulation of LIM-kinase 1 and cofilin in thrombin-stimulated platelets
Abstract
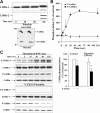
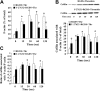
Cofilin is a regulator of actin filament dynamics. We studied whether during platelet activation Rho kinase stimulates LIM kinase (LIMK) leading to subsequent phosphorylation and inactivation of cofilin. Platelet shape change and aggregation/secretion were induced by low and high concentrations of thrombin, respectively. We found that during these platelet responses Rho kinase activation was responsible for mediating rapid Thr508 phosphorylation and activation of LIMK-1 and for the F-actin increase during shape change and, in part, during secretion. Surprisingly, during shape change cofilin phosphorylation was unaltered, and during aggregation/secretion cofilin was first rapidly dephosphorylated by an okadaic acid-insensitive phosphatase and then slowly rephosphorylated by LIMK-1. LIMK-1 phosphorylation and cofilin dephosphorylation and rephosphorylation during aggregation were independent of integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3) engagement. Cofilin phosphorylation did not regulate cofilin association with F-actin and was unrelated to the F-actin increase in thrombin-activated platelets. Our study identifies LIMK-1 as being activated by Rho kinase in thrombin-stimulated platelets. Two counteracting pathways, a cofilin phosphatase and LIMK-1, are activated during platelet aggregation/secretion regulating cofilin phosphorylation sequentially and independently of integrin alpha(IIb)beta(3) engagement. Rho kinase-mediated F-actin increase during platelet shape change and secretion involves a mechanism other than LIMK-1-mediated cofilin phosphorylation, raising the possibility of another LIMK substrate regulating platelet actin assembly.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Lysophosphatidic acid stimulation of platelets rapidly induces Ca2+-dependent dephosphorylation of cofilin that is independent of dense granule secretion and aggregation.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2007 May-Jun;38(3):269-79. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2007.01.002. Epub 2007 Feb 26. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2007. PMID: 17321765
-
Unraveling a novel Rac1-mediated signaling pathway that regulates cofilin dephosphorylation and secretion in thrombin-stimulated platelets.Blood. 2009 Jul 9;114(2):415-24. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-10-183582. Epub 2009 May 8. Blood. 2009. PMID: 19429871
-
Hyperosmotic stress induces Rho/Rho kinase/LIM kinase-mediated cofilin phosphorylation in tubular cells: key role in the osmotically triggered F-actin response.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009 Mar;296(3):C463-75. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00467.2008. Epub 2008 Dec 24. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19109524 Free PMC article.
-
Lim kinases, regulators of actin dynamics.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007;39(6):1071-6. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2006.11.011. Epub 2006 Nov 28. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17188549 Review.
-
Targeting ROCK/LIMK/cofilin signaling pathway in cancer.Arch Pharm Res. 2019 Jun;42(6):481-491. doi: 10.1007/s12272-019-01153-w. Epub 2019 Apr 27. Arch Pharm Res. 2019. PMID: 31030376 Review.
Cited by
-
Lysophosphatidic acid in atherosclerotic diseases.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Oct;167(3):465-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02021.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22568609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ROCK1 and LIMK2 interact in spread but not blebbing cancer cells.PLoS One. 2008;3(10):e3398. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0003398. Epub 2008 Oct 14. PLoS One. 2008. PMID: 18852895 Free PMC article.
-
Cucurbitacins Elicit Anti-Platelet Activity via Perturbation of the Cytoskeleton and Integrin Function.Thromb Haemost. 2022 Jul;122(7):1115-1129. doi: 10.1055/a-1788-5322. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Thromb Haemost. 2022. PMID: 35253142 Free PMC article.
-
Nischarin inhibits LIM kinase to regulate cofilin phosphorylation and cell invasion.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jun;28(11):3742-56. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01832-07. Epub 2008 Mar 10. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18332102 Free PMC article.
-
Mutations in the cofilin partner Aip1/Wdr1 cause autoinflammatory disease and macrothrombocytopenia.Blood. 2007 Oct 1;110(7):2371-80. doi: 10.1182/blood-2006-10-055087. Epub 2007 May 21. Blood. 2007. PMID: 17515402 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siess W. Molecular mechanisms of platelet activation. Physiol Rev. 1989;69: 58-178. - PubMed
-
- Fox JE. Regulation of platelet function by the cytoskeleton. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1993;344: 175-185. - PubMed
-
- Hartwig JH, Barkalow K, Azim A, Italiano J. The elegant platelet: signals controlling actin assembly. Thromb Haemost. 1999;82: 392-398. - PubMed
-
- Fox JE. Cytoskeletal proteins and platelet signaling. Thromb Haemost. 2001;86: 198-213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

