A role for the beta 1-beta 2 loop in the gating of 5-HT3 receptors
- PMID: 16221844
- PMCID: PMC6725699
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1045-05.2005
A role for the beta 1-beta 2 loop in the gating of 5-HT3 receptors
Abstract
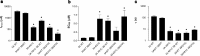
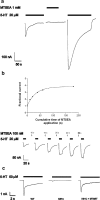
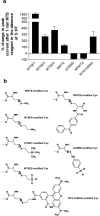
Based on the Torpedo acetylcholine receptor structure, Unwin and colleagues (Miyazawa et al., 2003; Unwin, 2005) hypothesized that the transduction of agonist binding to channel gate opening involves a "pin-into-socket" interaction between alphaV46 at the tip of the extracellular beta1-beta2 loop and the transmembrane M2 segment and M2-M3 loop. We mutated to cysteine the aligned positions in the 5-HT3A and 5-HT3B subunit beta1-beta2 loops K81 and Q70, respectively. The maximal 5-HT-activated currents in receptors containing 5-HT3A/K81C or 5-HT3B/Q70C were markedly reduced compared with wild type. Desensitization of wild-type currents involved fast and slow components. Mutant currents desensitized with only the fast time constant. Reaction with several methanethiosulfonate reagents potentiated currents to wild-type levels, but reaction with other more rigid thiol-reactive reagents caused inhibition. Single-channel conductances of wild type, K81C, and K81C after modification were similar. We tested the proximity of K81C to the M2-M3 loop by mutating M2-M3 loop residues to cysteine in the K81C background. Disulfide bonds formed in 5-HT3A/K81C/A304C and 5-HT3A/K81C/I305C when coexpressed with 5-HT3B. We conclude that in the resting state, K81 is not in a hydrophobic pocket as suggested by the pin-into-socket hypothesis. K81 interacts with the extracellular end of M2 and plays a critical role in channel opening and in the return from fast desensitization. We suggest that during channel activation, beta1-beta2 loop movement moves M2 and the M2-M3 loop so that the M2 segments rotate/translate away from the channel axis, thereby opening the lumen. Recovery from fast desensitization requires the interaction between K81 and the extracellular end of M2.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The interface between extracellular and transmembrane domains of homomeric Cys-loop receptors governs open-channel lifetime and rate of desensitization.J Neurosci. 2008 Jul 30;28(31):7808-19. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0448-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18667613 Free PMC article.
-
The 4'lysine in the putative channel lining domain affects desensitization but not the single-channel conductance of recombinant homomeric 5-HT3A receptors.J Physiol. 2000 Jan 15;522 Pt 2(Pt 2):187-98. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.00187.x. J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10639097 Free PMC article.
-
Length and amino acid sequence of peptides substituted for the 5-HT3A receptor M3M4 loop may affect channel expression and desensitization.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35563. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0035563. Epub 2012 Apr 23. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22539982 Free PMC article.
-
The 5-hydroxytryptamine type 3 (5-HT3) receptor reveals a novel determinant of single-channel conductance.Biochem Soc Trans. 2004 Jun;32(Pt3):547-52. doi: 10.1042/BST0320547. Biochem Soc Trans. 2004. PMID: 15157181 Review.
-
The 5-HT3 receptor--the relationship between structure and function.Neuropharmacology. 2009 Jan;56(1):273-84. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.08.003. Epub 2008 Aug 12. Neuropharmacology. 2009. PMID: 18761359 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Structural basis of activation of cys-loop receptors: the extracellular-transmembrane interface as a coupling region.Mol Neurobiol. 2009 Dec;40(3):236-52. doi: 10.1007/s12035-009-8084-x. Epub 2009 Oct 28. Mol Neurobiol. 2009. PMID: 19859835 Review.
-
Gating of nicotinic ACh receptors: latest insights into ligand binding and function.J Physiol. 2010 Feb 15;588(Pt 4):597-602. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.182691. Epub 2009 Nov 16. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19917567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation and desensitization induce distinct conformational changes at the extracellular-transmembrane domain interface of the glycine receptor.J Biol Chem. 2011 Nov 4;286(44):38814-38824. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.273631. Epub 2011 Sep 14. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21917927 Free PMC article.
-
The interface between extracellular and transmembrane domains of homomeric Cys-loop receptors governs open-channel lifetime and rate of desensitization.J Neurosci. 2008 Jul 30;28(31):7808-19. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0448-08.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18667613 Free PMC article.
-
Pathways and Barriers for Ion Translocation through the 5-HT3A Receptor Channel.PLoS One. 2015 Oct 14;10(10):e0140258. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140258. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26465896 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Absalom NL, Lewis TM, Kaplan W, Pierce KD, Schofield PR (2003) Role of charged residues in coupling ligand binding and channel activation in the extracellular domain of the glycine receptor. J Biol Chem 278: 50151-50157. - PubMed
-
- Absalom NL, Lewis TM, Schofield PR (2004) Mechanisms of channel gating of the ligand-gated ion channel superfamily inferred from protein structure. Exp Physiol 89: 145-153. - PubMed
-
- Bera AK, Chatav M, Akabas MH (2002) GABAA receptor M2-M3 loop secondary structure and changes in accessibility during channel gating. J Biol Chem 277: 43002-43010. - PubMed
-
- Bouzat C, Gumilar F, Spitzmaul G, Wang HL, Rayes D, Hansen SB, Taylor P, Sine SM (2004) Coupling of agonist binding to channel gating in an ACh-binding protein linked to an ion channel. Nature 430: 896-900. - PubMed
-
- Brejc K, van Dijk WJ, Klaassen RV, Schuurmans M, van Der Oost J, Smit AB, Sixma TK (2001) Crystal structure of an ACh-binding protein reveals the ligand-binding domain of nicotinic receptors. Nature 411: 269-276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
