Both laminin and Schwann cell dystroglycan are necessary for proper clustering of sodium channels at nodes of Ranvier
- PMID: 16221851
- PMCID: PMC1409814
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2068-05.2005
Both laminin and Schwann cell dystroglycan are necessary for proper clustering of sodium channels at nodes of Ranvier
Abstract
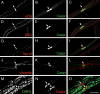
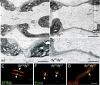
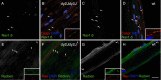
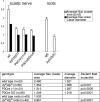
Nodes of Ranvier are specialized axonal domains, at which voltage-gated sodium channels cluster. How axons cluster molecules in discrete domains is mostly unknown. Both axons and glia probably provide constraining mechanisms that contribute to domain formation. Proper sodium channel clustering in peripheral nerves depends on contact from Schwann cell microvilli, where at least one molecule, gliomedin, binds the sodium channel complex and induces its clustering. Furthermore, mice lacking Schwann cell dystroglycan have aberrant microvilli and poorly clustered sodium channels. Dystroglycan could interact at the basal lamina or at the axonglial surface. Because dystroglycan is a laminin receptor, and laminin 2 mutations [merosin-deficient congenital muscular dystrophy (MDC1A)] cause reduced nerve conduction velocity, we asked whether laminins are involved. Here, we show that the composition of both laminins and the dystroglycan complex at nodes differs from that of internodes. Mice defective in laminin 2 have poorly formed microvilli and abnormal sodium clusters. These abnormalities are similar, albeit less severe, than those of mice lacking dystroglycan. However, mice lacking all Schwann cell laminins show severe nodal abnormalities, suggesting that other laminins compensate for the lack of laminin 2. Thus, although laminins are located at a distance from the axoglial junction, they are required for proper clustering of sodium channels. Laminins, through their specific nodal receptors and cytoskeletal linkages, may participate in the formation of mechanisms that constrain clusters at nodes. Finally, abnormal sodium channel clusters are present in a patient with MDC1A, providing a molecular basis for the reduced nerve conduction velocity in this disorder.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Perlecan is recruited by dystroglycan to nodes of Ranvier and binds the clustering molecule gliomedin.J Cell Biol. 2015 Feb 2;208(3):313-29. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201403111. J Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25646087 Free PMC article.
-
Unique role of dystroglycan in peripheral nerve myelination, nodal structure, and sodium channel stabilization.Neuron. 2003 Jun 5;38(5):747-58. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(03)00301-5. Neuron. 2003. PMID: 12797959
-
Dependence of nodal sodium channel clustering on paranodal axoglial contact in the developing CNS.J Neurosci. 1999 Sep 1;19(17):7516-28. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-17-07516.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10460258 Free PMC article.
-
The local differentiation of myelinated axons at nodes of Ranvier.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003 Dec;4(12):968-80. doi: 10.1038/nrn1253. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003. PMID: 14682359 Review.
-
[New insights on the organization of the nodes of Ranvier].Rev Neurol (Paris). 2014 Dec;170(12):819-24. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2014.03.017. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2014. PMID: 25459119 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Autoimmune antigenic targets at the node of Ranvier in demyelinating disorders.Nat Rev Neurol. 2015 Mar;11(3):143-56. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2014.260. Epub 2015 Jan 27. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25623793 Review.
-
The olfactomedin domain from gliomedin is a β-propeller with unique structural properties.J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 6;290(6):3612-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.627547. Epub 2014 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25525261 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of sodium channel clustering and its influence on axonal impulse conduction.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016 Feb;73(4):723-35. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-2081-1. Epub 2015 Oct 29. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2016. PMID: 26514731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Brain Dysfunction in LAMA2-Related Congenital Muscular Dystrophy: Lessons From Human Case Reports and Mouse Models.Front Mol Neurosci. 2020 Jul 23;13:118. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00118. eCollection 2020. Front Mol Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32792907 Free PMC article.
-
The Adult Murine Intestine is Dependent on Constitutive Laminin-γ1 Synthesis.Sci Rep. 2019 Dec 17;9(1):19303. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-55844-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31848396 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boiko T, Rasband MN, Levinson SR, Caldwell JH, Mandel G, Trimmer JS, Matthews G (2001) Compact myelin dictates the differential targeting of two sodium channel isoforms in the same axon. Neuron 30: 91-104. - PubMed
-
- Bradley WG, Jenkison M (1973) Abnormalities of peripheral nerves in murine muscular dystrophy. J Neurol Sci 18: 227-247. - PubMed
-
- Bradley WG, Jenkison M (1975) Neural abnormalities in the dystrophic mouse. J Neurol Sci 25: 249-255. - PubMed
-
- Bradley WG, Jaros E, Jenkison M (1977) The nodes of Ranvier in the nerves of mice with muscular dystrophy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 36: 797-806. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
