Cisplatin-incorporating polymeric micelles (NC-6004) can reduce nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity of cisplatin in rats
- PMID: 16222314
- PMCID: PMC2361620
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602772
Cisplatin-incorporating polymeric micelles (NC-6004) can reduce nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity of cisplatin in rats
Abstract
In spite of the clinical usefulness of cisplatin (CDDP), there are many occasions in which it is difficult to continue the administration of CDDP due to its nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity. We examined the incorporation of CDDP into polymeric micelles to see if this allowed the resolution of these disadvantages. Cisplatin was incorporated into polymeric micelles through the polymer-metal complex formation between polyethylene glycol poly(glutamic acid) block copolymers and CDDP (NC-6004). The pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and toxicity studies of CDDP and NC-6004 were conducted in rats or mice. The particle size of NC-6004 was approximately 30 nm, with a narrow size distribution. In rats, the area under the curve and total body clearance values for NC-6004 were 65-fold and one-nineteenth the values for CDDP (P<0.001 and 0.01, respectively). In MKN-45-implanted mice, NC-6004 tended to show antitumour activity, which was comparable to or greater than that of CDDP. Histopathological and biochemical studies revealed that NC-6004 significantly inhibited the nephrotoxicity of CDDP. On the other hand, blood biochemistry revealed transient hepatotoxicity on day 7 after the administration of NC-6004. Furthermore, rats given CDDP showed a significant delay (P<0.05) in sensory nerve conduction velocity in their hind paws as compared with rats given NC-6004. Electron microscopy in rats given CDDP indicated the degeneration of the sciatic nerve, but these findings were not seen in rats given NC-6004. These results were presumably attributable to the significantly reduced accumulation of platinum in nerve tissue when NC-6004 was administered (P<0.05). NC-6004 preserved the antitumour activity of CDDP and reduced its nephrotoxicity and neurotoxicity, which would therefore seem to suggest that NC-6004 could allow the long-term administration of CDDP where caution against hepatic dysfunction must be exercised.
Figures
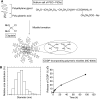

 ), liver (□), spleen (
), liver (□), spleen ( ), and lung (▪)). (D) Time profiles of Pt concentration in the MKN-45 solid tumour after a single i.v. injection of CDDP (▪) and NC-6004 (□) in MKN-45 bearing BALB/c nude mice (n=3). Values are expressed as the mean±s.d.
), and lung (▪)). (D) Time profiles of Pt concentration in the MKN-45 solid tumour after a single i.v. injection of CDDP (▪) and NC-6004 (□) in MKN-45 bearing BALB/c nude mice (n=3). Values are expressed as the mean±s.d.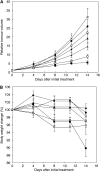

 ), and at a dose of 15 mg kg−1 on a CDDP basis (
), and at a dose of 15 mg kg−1 on a CDDP basis ( ) (n=8) to rats. Histopathological changes in the kidney on day 7 after the i.v. injection of CDDP (C, × 4) and NC-6004 (D, × 4) in rats at an equivalent dose of 10 mg kg−1 CDDP. In rats given CDDP, widespread tubular degeneration as indicated by tubular dilation with flattening of the lining cells of tubular epithelium was seen. On the other hand, no histopathological change was observed in the kidney from all animals in the NC-6004 10 mg kg−1 administration group. For hepatotoxicity (E), the plasma concentrations of GOT and GPT were measured on day 7 after administration. When administering NC-6004 at a dose of 10 mg kg−1 on a CDDP basis, five of 13 blood samples were taken on day 14 after administration (
) (n=8) to rats. Histopathological changes in the kidney on day 7 after the i.v. injection of CDDP (C, × 4) and NC-6004 (D, × 4) in rats at an equivalent dose of 10 mg kg−1 CDDP. In rats given CDDP, widespread tubular degeneration as indicated by tubular dilation with flattening of the lining cells of tubular epithelium was seen. On the other hand, no histopathological change was observed in the kidney from all animals in the NC-6004 10 mg kg−1 administration group. For hepatotoxicity (E), the plasma concentrations of GOT and GPT were measured on day 7 after administration. When administering NC-6004 at a dose of 10 mg kg−1 on a CDDP basis, five of 13 blood samples were taken on day 14 after administration ( ). The other samples were taken on day 7 administration. In the group given CDDP at a dose of 10 mg kg−1, four of 12 rats died within 7 days. Values are expressed as the mean±s.d. *P<0.05, **P<0.001, NS: not significant.
). The other samples were taken on day 7 administration. In the group given CDDP at a dose of 10 mg kg−1, four of 12 rats died within 7 days. Values are expressed as the mean±s.d. *P<0.05, **P<0.001, NS: not significant.
 ), CDDP (•), and NC-6004 (□)). Histopathological changes of the sciatic nerve were examined by electron microscopy after the administration of CDDP (B) and NC-6004 (C). In rats given CDDP, widespread degenerations as indicated by loss of microtubules, loss of filaments, degeneration in the cytoplasm of Schwann cells (
), CDDP (•), and NC-6004 (□)). Histopathological changes of the sciatic nerve were examined by electron microscopy after the administration of CDDP (B) and NC-6004 (C). In rats given CDDP, widespread degenerations as indicated by loss of microtubules, loss of filaments, degeneration in the cytoplasm of Schwann cells ( ), and an irregular inner loop (
), and an irregular inner loop ( ) were seen. On the other hand, animals given NC-6004 exhibited nearly normal electron micrographs of the sciatic nerve as the control animals. (D) Changes in relative body weight. Data were derived from the same rats as those used in the present study (control (×), CDDP (•), and NC-6004 (○)). (E) The Pt concentration in the sciatic nerve. Rats were given CDDP (▪) (5 mg kg−1, n=5), NC-6004 (□) (an equivalent dose of 5 mg kg−1 CDDP, n=5), or 5% glucose (n=2), all i.v. twice a week, four administrations in total. On day 3 after the final administration, a segment of the sciatic nerve was removed and the Pt concentration in the sciatic nerve was measured by ICP-MS. Body weight changes are expressed as the mean±s.e. The other data are expressed as the mean±s.d. *P<0.05, **P<0.001, NS: not significant.
) were seen. On the other hand, animals given NC-6004 exhibited nearly normal electron micrographs of the sciatic nerve as the control animals. (D) Changes in relative body weight. Data were derived from the same rats as those used in the present study (control (×), CDDP (•), and NC-6004 (○)). (E) The Pt concentration in the sciatic nerve. Rats were given CDDP (▪) (5 mg kg−1, n=5), NC-6004 (□) (an equivalent dose of 5 mg kg−1 CDDP, n=5), or 5% glucose (n=2), all i.v. twice a week, four administrations in total. On day 3 after the final administration, a segment of the sciatic nerve was removed and the Pt concentration in the sciatic nerve was measured by ICP-MS. Body weight changes are expressed as the mean±s.e. The other data are expressed as the mean±s.d. *P<0.05, **P<0.001, NS: not significant.References
-
- Allen TM (1994) Long-circulating (sterically stabilized) liposomes for targeted drug delivery. Trends Pharmacol Sci 15: 215–220 - PubMed
-
- Bellmunt J, Ribas A, Eres N, Albanell J, Almanza C, Bermejo B, Sole LA, Baselga J (1997) Carboplatin-based versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy in the treatment of surgically incurable advanced bladder carcinoma. Cancer 80: 1966–1972 - PubMed
-
- Boulikas T, Vougiouka M (2004) Recent clinical trials using cisplatin, carboplatin and their combination chemotherapy drugs (review). Oncol Rep 11: 559–595 - PubMed
-
- Cassidy J, Tabernero J, Twelves C, Brunet R, Butts C, Conroy T, Debraud F, Figer A, Grossmann J, Sawada N, Schoffski P, Sobrero A, Van Cutsem E, Diaz-Rubio E (2004) XELOX (capecitabine plus oxaliplatin): active first-line therapy for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol 22: 2084–2091 - PubMed
-
- Cavaletti G, Tredici G, Marmiroli P, Petruccioli MG, Barajon I, Fabbrica D (1992) Morphometric study of the sensory neuron and peripheral nerve changes induced by chronic cisplatin (DDP) administration in rats. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 84: 364–371 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

