Study of transactivating effect of pre-S2 protein of hepatitis B virus and cloning of genes transactivated by pre-S2 protein with suppression subtractive hybridization
- PMID: 16222733
- PMCID: PMC4320350
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i35.5438
Study of transactivating effect of pre-S2 protein of hepatitis B virus and cloning of genes transactivated by pre-S2 protein with suppression subtractive hybridization
Abstract
Aim: To investigate the transactivating effect of pre-S2 protein of hepatitis B virus (HBV) and construct a subtractive cDNA library of genes transactivated by pre-S2 protein with suppression subtractive hybridization (SSH) technique, and to pave the way for elucidating the pathogenesis of HBV infection.
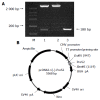
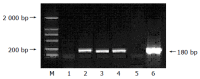
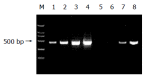
Methods: pcDNA3.1(-)-pre-S2 containing pre-S2 region of HBV genome was constructed by routine molecular methods. HepG2 cells were cotransfected with pcDNA3.1(-)-pre-S2/pSV-lacZ and empty pcDNA3.1(-)/pSV-lacZ. After 48 h, cells were collected and detected for the expression of beta-galactosidase (beta-gal). SSH and bioinformatics techniques were used, the mRNA of HepG2 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1(-)-pre-S2 and pcDNA3.1(-) empty vector was isolated, respectively, cDNA was synthesized. After digestion with restriction enzyme RsaI, cDNA fragments were obtained. Tester cDNA was then divided into two groups and ligated to the specific adaptor 1 and adaptor 2, respectively. After tester cDNA was hybridized with driver cDNA twice and underwent two times of nested PCR, amplified cDNA fragments were subcloned into pGEM-Teasy vectors to set up the subtractive library. Amplification of the library was carried out with E.coli strain DH5alpha. The cDNA was sequenced and analyzed in GenBank with Blast search after PCR.
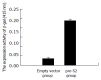
Results: The pre-S2 mRNA could be detected in HepG2 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1(-)-pre-S2 plasmid. The activity of beta-gal in HepG2 cells transfected with pcDNA3.1(-)-pre-S2/pSV-lacZ was 7.0 times higher than that of control plasmid (P<0.01). The subtractive library of genes transactivated by HBV pre-S2 protein was constructed successfully. The amplified library contains 96 positive clones. Colony PCR showed that 86 clones contained 200-1 000 bp inserts. Sequence analysis was performed in 50 clones randomly, and the full length sequences were obtained with bioinformatics method and searched for homologous DNA sequence from GenBank, altogether 25 coding sequences were obtained, these cDNA sequences might be the target genes transactivated by pre-S2 protein.
Conclusion: The pre-S2 protein of HBV has transactivating effect on SV40 early promoter. The obtained sequences may be target genes transactivated by pre-S2 protein among which some genes coding proteins involved in cell cycle regulation, metabolism, immunity, signal transduction and cell apoptosis. This finding brings some new clues for studying the biological functions of pre-S2 protein and further understanding of HBV hepatocarcinogesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transactivating effect of complete S protein of hepatitis B virus and cloning of genes transactivated by complete S protein using suppression subtractive hybridization technique.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Jul 7;11(25):3893-8. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i25.3893. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 15991289 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and cloning for proteins transactivated by the PS1TP5 protein of hepatitis B virus: a suppression subtractive hybridization study.World J Gastroenterol. 2007 Mar 14;13(10):1602-7. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i10.1602. World J Gastroenterol. 2007. PMID: 17461456 Free PMC article.
-
[Screening and cloning target genes transactivated by hepatitis C virus F protein using suppression subtractive hybridization technique].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2005 Sep;13(9):660-3. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2005. PMID: 16174453 Chinese.
-
[Cloning of genes transactivated by hepatitis B virus X protein].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2003 Jan;11(1):5-7. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 12546730 Chinese.
-
The isolation and identification of cDNA genes by their heterologous expression and function.Genet Eng (N Y). 1990;12:297-316. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-0641-2_15. Genet Eng (N Y). 1990. PMID: 1366706 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of the Functional Role of TIMM29 in the Hepatitis B Virus Life Cycle.Microbiol Immunol. 2025 Apr;69(4):229-246. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.13206. Epub 2025 Feb 16. Microbiol Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39956808 Free PMC article.
-
A Rapid Immunochromatographic Method Based on a Secondary Antibody-Labelled Magnetic Nanoprobe for the Detection of Hepatitis B preS2 Surface Antigen.Biosensors (Basel). 2020 Oct 31;10(11):161. doi: 10.3390/bios10110161. Biosensors (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33142715 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shouval D. Hepatitis B vaccines. J Hepatol. 2003;39:S70–S76. - PubMed
-
- Humphries JC, Dixon JS. Antivirals for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: current and future options. Intervirology. 2003;46:413–420. - PubMed
-
- Colombo M, Sangiovanni A. Etiology, natural history and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Antiviral Res. 2003;60:145–150. - PubMed
-
- Gjørup IE, Skinhøj P. New aspects on the natural history of chronic hepatitis B infection: implication for therapy. Scand J Infect Dis. 2003;35:808–813. - PubMed
-
- Dong J, Cheng J, Wang Q, Shi S, Wang G, Si C. Cloning and analysis of the genomic DNA sequence of augmenter of liver regeneration from rat. Chin Med Sci J. 2002;17:63–67. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

