Cancer-derived VEGF plays no role in malignant ascites formation in the mouse
- PMID: 16222736
- PMCID: PMC4320353
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i35.5455
Cancer-derived VEGF plays no role in malignant ascites formation in the mouse
Abstract
Aim: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is a potent mediator of peritoneal fluid accumulation following tumor progression. This study investigated the role of VEGF secreted by cancerous cells in the formation of malignant ascites.
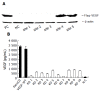
Methods: VEGF expression was eliminated by knockdown in the pancreas cancer cell-line PancO2 using vector-based short-hairpin type RNA interference (RNAi). Malignant ascites formation in the mouse was analyzed by intraperitoneal injection of PancO2 cells expressing VEGF or with expression knockdown.
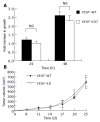
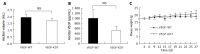
Results: The VEGF knockdown PancO2 cell was successfully established. Knockdown of VEGF did not affect cancer cell proliferation in vitro or in vivo. The volume of ascites following peritoneal expansion of the tumor in VEGF knockdown cells and control cells did not differ statistically in this in vivo study. Moreover, the VEGF concentration in the ascites did not differ statistically.
Conclusion: Malignant ascites formation might be mediated by VEGF production in noncancerous tissues, such as stromal compartments. An anti-VEGF strategy against malignant ascites could be applied to various tumors regardless of whether they secrete VEGF.
Figures
References
-
- Yeo KT, Wang HH, Nagy JA, Sioussat TM, Ledbetter SR, Hoogewerf AJ, Zhou Y, Masse EM, Senger DR, Dvorak HF. Vascular permeability factor (vascular endothelial growth factor) in guinea pig and human tumor and inflammatory effusions. Cancer Res. 1993;53:2912–2918. - PubMed
-
- Senger DR, Galli SJ, Dvorak AM, Perruzzi CA, Harvey VS, Dvorak HF. Tumor cells secrete a vascular permeability factor that promotes accumulation of ascites fluid. Science. 1983;219:983–985. - PubMed
-
- Akutagawa N, Nishikawa A, Iwasaki M, Fujimoto T, Teramoto M, Kitajima Y, Endo T, Shibuya M, Kudo R. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and E-cadherin in human ovarian cancer: association with ascites fluid accumulation and peritoneal dissemination in mouse ascites model. Jpn J Cancer Res. 2002;93:644–651. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

