A novel form of immune signaling revealed by transmission of the inflammatory mediator serotonin between dendritic cells and T cells
- PMID: 16223770
- PMCID: PMC1895901
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-07-2903
A novel form of immune signaling revealed by transmission of the inflammatory mediator serotonin between dendritic cells and T cells
Abstract
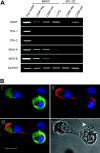
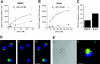
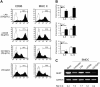
Adaptive immunity is triggered at the immune synapse, where peptide-major histocompatibility complexes and costimulatory molecules expressed by dendritic cells (DCs) are physically presented to T cells. Here we describe transmission of the inflammatory monoamine serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine [5-HT]) between these cells. DCs take up 5-HT from the microenvironment and from activated T cells (that synthesize 5-HT) and this uptake is inhibited by the antidepressant, fluoxetine. Expression of 5-HT transporters (SERTs) is regulated by DC maturation, exposure to microbial stimuli, and physical interactions with T cells. Significantly, 5-HT sequestered by DCs is stored within LAMP-1+ vesicles and subsequently released via Ca2+-dependent exocytosis, which was confirmed by amperometric recordings. In turn, extracellular 5-HT can reduce T-cell levels of cAMP, a modulator of T-cell activation. Thus, through the uptake of 5-HT at sites of inflammation, and from activated T cells, DCs may shuttle 5-HT to naive T cells and thereby modulate T-cell proliferation and differentiation. These data constitute the first direct measurement of triggered exocytosis by DCs and reveal a new and rapid type of signaling that may be optimized by the intimate synaptic environment between DCs and T cells. Moreover, these results highlight an important role for 5-HT signaling in immune function and the potential consequences of commonly used drugs that target 5-HT uptake and release.
Figures

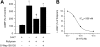

References
-
- Steinman RM. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9: 271-296. - PubMed
-
- Pulendran B, Banchereau J, Maraskovsky E, Maliszewski C. Modulating the immune response with dendritic cells and their growth factors. Trends Immunol. 2001;22: 41-47. - PubMed
-
- Iwasaki A, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptor control of the adaptive immune responses. Nat Immunol. 2004;5: 987-995. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y, Evans JE, Rock KL. Molecular identification of a danger signal that alerts the immune system to dying cells. Nature. 2003;425: 516-521. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

