Physiologic self antigens rapidly capacitate autoimmune disease-specific polyclonal CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells
- PMID: 16223778
- PMCID: PMC1895904
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2005-08-3088
Physiologic self antigens rapidly capacitate autoimmune disease-specific polyclonal CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells
Abstract
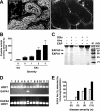
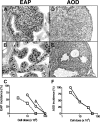
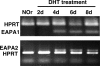
Studies on CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells (Tregs) with transgenic T-cell receptors indicate that Tregs may receive continuous antigen (Ag) stimulation in the periphery. However, the consequence of this Ag encounter and its relevance to physiologic polyclonal Treg function are not established. In autoimmune prostatitis (EAP) of the day-3 thymectomized (d3tx) mice, male Tregs suppressed EAP 3 times better than Tregs from female mice or male mice without prostates. Importantly, the superior EAP-suppressing function was acquired after a 6-day exposure to prostate Ag in the periphery, unaffected by sex hormones. Thus, a brief exposure of physiologic prostate Ag capacitates peripheral polyclonal Tregs to suppress EAP. In striking contrast, autoimmune ovarian disease (AOD) was suppressed equally by male and female Tregs. We now provide evidence that the ovarian Ag develops at birth, 14 days earlier than prostate Ag, and that male Tregs respond to neonatal ovarian Ag in the Treg recipients to gain AOD-suppressing capacity. When d3tx female recipients were deprived of ovarian Ag in the neonatal period, AOD was suppressed by female but not by male Tregs, whereas dacryoadenitis was suppressed by both. We conclude that the physiologic autoAg quickly and continuously enhances disease-specific polyclonal Treg function to maintain self-tolerance.
Figures

References
-
- Sakaguchi S, Sakaguchi N, Asano M, Itoh M, Toda M. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes various autoimmune diseases. J Immunol. 1995;155: 1151-1164. - PubMed
-
- Fontenot JD, Gavin MA, Rudensky AY. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat Immunol. 2003;4: 330-336. - PubMed
-
- Alard P, Thompson C, Agersborg SS, et al. Endogenous oocyte antigens are required for rapid induction and progression of autoimmune ovarian disease following day-3 thymectomy. J Immunol. 2001;166: 4363-4369. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

