Structure and properties of alpha-synuclein and other amyloids determined at the amino acid level
- PMID: 16223878
- PMCID: PMC1266128
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0507405102
Structure and properties of alpha-synuclein and other amyloids determined at the amino acid level
Abstract
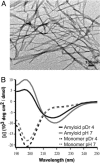
The structure of alpha-synuclein (alpha-syn) amyloid was studied by hydrogen-deuterium exchange by using a fragment separation-MS analysis. The conditions used made it possible to distinguish the exchange of unprotected and protected amide hydrogens and to define the order/disorder boundaries at close to amino acid resolution. The soluble alpha-syn monomer exchanges its amide hydrogens with water hydrogens at random coil rates, consistent with its natively unstructured condition. In assembled amyloid, long N-terminal and C-terminal segments remain unprotected (residues 1- approximately 38 and 102-140), although the N-terminal segment shows some heterogeneity. A continuous middle segment (residues approximately 39-101) is strongly protected by systematically H-bonded cross-beta structure. This segment is much too long to fit the amyloid ribbon width, but non-H-bonded amides expected for direction-changing loops are not apparent. These results and other known constraints specify that alpha-syn amyloid adopts a chain fold like that suggested before for amyloid-beta [Petkova et al. (2002) Proc. Natl. Acad Sci. USA 99, 16742-16747] but with a short, H-bonded interlamina turn. More generally, we suggest that the prevalence of accidental amyloid formation derives mainly from the exceptional ability of the main chain in a structurally relaxed beta-conformation to adapt to and energy-minimize side-chain mismatching. Seeding specificity, strain variability, and species barriers then arise because newly added parallel in-register chains must faithfully reproduce the same set of adaptations.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Beta-sheet core of human prion protein amyloid fibrils as determined by hydrogen/deuterium exchange.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Jan 30;104(5):1510-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0608447104. Epub 2007 Jan 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17242357 Free PMC article.
-
Secondary structural formation of alpha-synuclein amyloids as revealed by g-factor of solid-state circular dichroism.Biopolymers. 2006 Oct 15;83(3):226-32. doi: 10.1002/bip.20550. Biopolymers. 2006. PMID: 16752390
-
Amide hydrogen exchange determined by mass spectrometry: application to rabbit muscle aldolase.Biochemistry. 1996 Jan 23;35(3):779-91. doi: 10.1021/bi952227q. Biochemistry. 1996. PMID: 8547258
-
Protein denaturation and aggregation: Cellular responses to denatured and aggregated proteins.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005 Dec;1066:181-221. doi: 10.1196/annals.1363.030. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2005. PMID: 16533927 Review.
-
Measuring the hydrogen/deuterium exchange of proteins at high spatial resolution by mass spectrometry: overcoming gas-phase hydrogen/deuterium scrambling.Acc Chem Res. 2014 Oct 21;47(10):3018-27. doi: 10.1021/ar500194w. Epub 2014 Aug 29. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 25171396 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural determinants of phenotypic diversity and replication rate of human prions.PLoS Pathog. 2015 Apr 14;11(4):e1004832. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004832. eCollection 2015 Apr. PLoS Pathog. 2015. PMID: 25875953 Free PMC article.
-
Hsp104 antagonizes alpha-synuclein aggregation and reduces dopaminergic degeneration in a rat model of Parkinson disease.J Clin Invest. 2008 Sep;118(9):3087-97. doi: 10.1172/JCI35781. J Clin Invest. 2008. PMID: 18704197 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the conformation of a prion protein fibril with hydrogen exchange.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 15;285(42):32303-11. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.114504. Epub 2010 Aug 2. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20679344 Free PMC article.
-
Many overlapping peptides for protein hydrogen exchange experiments by the fragment separation-mass spectrometry method.J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2011 Nov;22(11):1898-905. doi: 10.1007/s13361-011-0235-4. Epub 2011 Sep 14. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom. 2011. PMID: 21952777 Free PMC article.
-
Development of in vivo HDX-MS with applications to a TonB-dependent transporter and other proteins.Protein Sci. 2022 Sep;31(9):e4402. doi: 10.1002/pro.4402. Protein Sci. 2022. PMID: 36040258 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Eanes, E. D. & Glenner, G. G. (1968) J. Histochem. Cytochem. 16, 673-677. - PubMed
-
- Sunde, M. & Blake, C. C. (1997) Adv. Protein Chem. 50, 123-159. - PubMed
-
- Sunde, M. & Blake, C. C. (1998) Q. Rev. Biophys. 31, 1-39. - PubMed
-
- Benzinger, T. L., Gregory, D. M., Burkoth, T. S., Miller-Auer, H., Lynn, D. G., Botto, R. E. & Meredith, S. C. (2000) Biochemistry 39, 3491-3499. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

