H-ras, K-ras, and inner plasma membrane raft proteins operate in nanoclusters with differential dependence on the actin cytoskeleton
- PMID: 16223883
- PMCID: PMC1266090
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0504114102
H-ras, K-ras, and inner plasma membrane raft proteins operate in nanoclusters with differential dependence on the actin cytoskeleton
Abstract
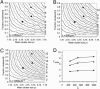
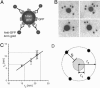
Plasma membrane compartmentalization imposes lateral segregation on membrane proteins that is important for regulating signal transduction. We use computational modeling of immunogold spatial point patterns on intact plasma membrane sheets to test different models of inner plasma membrane organization. We find compartmentalization at the nanoscale level but show that a classical raft model of preexisting stable domains into which lipid raft proteins partition is incompatible with the spatial point patterns generated by the immunogold labeling of a palmitoylated raft marker protein. Rather, approximately 30% of the raft protein exists in cholesterol-dependent nanoclusters, with approximately 70% distributed as monomers. The cluster/monomer ratio (number of proteins in clusters/number of proteins outside clusters) is independent of expression level. H-rasG12V and K-rasG12V proteins also operate in nanoclusters with fixed cluster/monomer ratios that are independent of expression level. Detailed calibration of the immunogold imaging protocol suggests that radii of raft and RasG12V protein nanoclusters may be as small as 11 and 6 nm, respectively, and shows that the nanoclusters contain small numbers (6.0-7.7) of proteins. Raft nanoclusters do not form if the actin cytoskeleton is disassembled. The formation of K-rasG12V but not H-rasG12V nanoclusters also is actin-dependent. K-rasG12V but not H-rasG12V signaling is abrogated by actin cytoskeleton disassembly, which shows that nanoclustering is critical for Ras function. These findings argue against stable preexisting domains on the inner plasma membrane in favor of dynamic actively regulated nanoclusters similar to those proposed for the outer plasma membrane. RasG12V nanoclusters may facilitate the assembly of essential signal transduction complexes.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

