The Herpesvirus saimiri replication and transcription activator acts synergistically with CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha to activate the DNA polymerase promoter
- PMID: 16227275
- PMCID: PMC1262591
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.79.21.13548-13560.2005
The Herpesvirus saimiri replication and transcription activator acts synergistically with CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha to activate the DNA polymerase promoter
Abstract
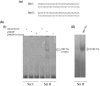
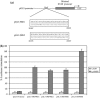
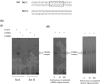
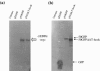
The open reading frame (ORF) 50 gene product, also known as the replication and transcription activator (Rta), is an immediate-early gene which is well conserved among all gamma-2 herpesviruses and plays a pivotal role in regulating the latent-lytic switch. Herpesvirus saimiri (HVS) ORF 50a functions as a sequence-specific transactivator capable of activating delayed-early (DE) gene expression via binding directly to an ORF 50 response element (RE) within the respective promoter. Analysis of the ORF 50 REs have identified two distinct types within HVS gene promoters. The first comprises a consensus sequence motif, CCN(9)GG, the second an AT-rich sequence. Here we demonstrate that ORF 50a is capable of transactivating the DE ORF 9 promoter which encodes the DNA polymerase. Deletion analysis of the ORF 9 promoter mapped the ORF 50 RE to a 95-bp region situated 126 bp upstream of the initiation codon. Gel retardation analysis further mapped the RE to a 28-bp fragment, which was able to confer ORF 50 responsiveness on an enhancerless simian virus 40 minimal promoter. Furthermore, sequence analysis identified multiple CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha (C/EBPalpha) binding sites within the ORF 9 promoter and specifically two within the close vicinity of the AT-rich ORF 50 RE. Analysis demonstrated that the HVS ORF 50a and C/EBPalpha proteins associate with the ORF 9 promoter in vivo, interact directly, and synergistically activate the ORF 9 promoter by binding to adjacent binding motifs. Overall, these data suggest a cooperative interaction between HVS ORF 50a and C/EBPalpha proteins to activate the DNA polymerase promoter during early stages of the lytic replication cycle.
Figures






Similar articles
-
The herpesvirus saimiri Rta gene autostimulates via binding to a non-consensus response element.J Gen Virol. 2005 Mar;86(Pt 3):581-587. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.80723-0. J Gen Virol. 2005. PMID: 15722517
-
Herpesvirus saimiri open reading frame 50 (Rta) protein reactivates the lytic replication cycle in a persistently infected A549 cell line.J Virol. 2001 Apr;75(8):4008-13. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.8.4008-4013.2001. J Virol. 2001. PMID: 11264393 Free PMC article.
-
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein-alpha is induced during the early stages of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) lytic cycle reactivation and together with the KSHV replication and transcription activator (RTA) cooperatively stimulates the viral RTA, MTA, and PAN promoters.J Virol. 2003 Sep;77(17):9590-612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.77.17.9590-9612.2003. J Virol. 2003. PMID: 12915572 Free PMC article.
-
gamma-2 Herpes virus post-transcriptional gene regulation.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006 Feb;12(2):110-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-0691.2005.01317.x. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2006. PMID: 16441447 Review.
-
Herpesvirus saimiri ORF57: a post-transcriptional regulatory protein.Front Biosci. 2008 Jan 1;13:2928-38. doi: 10.2741/2898. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 17981766 Review.
Cited by
-
A protein encoded by the bovine herpesvirus 1 latency-related gene interacts with specific cellular regulatory proteins, including CCAAT enhancer binding protein alpha.J Virol. 2007 Jan;81(1):59-67. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01171-06. Epub 2006 Sep 20. J Virol. 2007. PMID: 16987965 Free PMC article.
-
The cellular transcription factor, CCAAT enhancer-binding protein alpha (C/EBP-alpha), has the potential to activate the bovine herpesvirus 1 immediate-early transcription unit 1 promoter.J Neurovirol. 2009 Apr;15(2):123-30. doi: 10.1080/13550280802534771. J Neurovirol. 2009. PMID: 19115128
References
-
- Biesinger, B., J. J. Trimble, R. C. Desrosiers, and B. Fleckenstein. 1990. The divergence between two oncogenic herpesvirus saimiri strains in a genomic region related to the transforming phenotype. Virology 176:505-514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

