A gain-of-function allele of cbp-1, the Caenorhabditis elegans ortholog of the mammalian CBP/p300 gene, causes an increase in histone acetyltransferase activity and antagonism of activated Ras
- PMID: 16227593
- PMCID: PMC1265831
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.25.21.9427-9434.2005
A gain-of-function allele of cbp-1, the Caenorhabditis elegans ortholog of the mammalian CBP/p300 gene, causes an increase in histone acetyltransferase activity and antagonism of activated Ras
Abstract
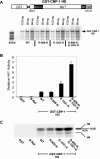
An RTK-Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway plays a key role in vulval induction in Caenorhabditis elegans. We have previously carried out screens for suppressors of activated Ras to identify factors that play critical roles in the regulation of the pathway. ku258 was isolated as a semidominant allele that suppresses the Multivulva phenotype caused by activated let-60 ras. Our genetic and molecular analyses indicate that ku258 is a gain-of-function allele resulting from two point mutations in the C. elegans homolog of the transcriptional coactivator p300/CBP, cbp-1. Genetic data also suggest that cbp-1 may act downstream of the Ras signaling pathway, but not primarily downstream of the Wnt signaling pathway, to negatively regulate vulval cell fate specification. cbp-1 may function in concert with LIN-1, an Ets transcription factor family member that is one of the targets of MAPK. In vitro histone acetylation assays have revealed that together, the two point mutations cause a sevenfold increase in the histone acetyltransferase (HAT) activity of recombinant CBP-1. To our knowledge, this is the only such HAT activity mutation isolated in a CBP/p300 family protein, and this mutation may define a negative role of the HAT activity in antagonizing Ras function in a specific developmental event.
Figures


References
-
- Ait-Si-Ali, S., D. Carlisi, S. Ramirez, L. C. Upegui-Gonzalez, A. Duquet, P. Robin, B. Rudkin, A. Harel-Bellan, and D. Trouche. 1999. Phosphorylation by p44 MAP kinase/ERK1 stimulates CBP histone acetyl transferase activity in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 262:157-162. - PubMed
-
- Ait-Si-Ali, S., S. Ramirez, F. X. Barre, F. Dkhissi, L. Magnaghi-Jaulin, J. A. Girault, P. Robin, M. Knibiehler, L. L. Pritchard, B. Ducommun, D. Trouche, and A. Harel-Bellan. 1998. Histone acetyltransferase activity of CBP is controlled by cycle-dependent kinases and oncoprotein E1A. Nature 396:184-186. - PubMed
-
- Bannister, A. J., and T. Kouzarides. 1996. The CBP co-activator is a histone acetyltransferase. Nature 384:641-643. - PubMed
-
- Beitel, G. J., S. Tuck, I. Greenwald, and H. R. Horvitz. 1995. The Caenorhabditis elegans gene lin-1 encodes an ETS-domain protein and defines a branch of the vulval induction pathway. Genes Dev. 9:3149-3162. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
