Overlapping intracellular and differential synaptic distributions of dopamine D1 and glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat nucleus accumbens
- PMID: 16228995
- PMCID: PMC2605084
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.20740
Overlapping intracellular and differential synaptic distributions of dopamine D1 and glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in rat nucleus accumbens
Abstract
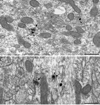
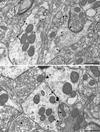
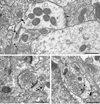
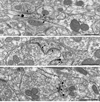
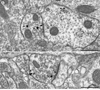
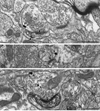
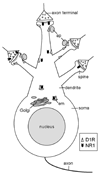
The dopamine D1 receptor (D1R) in the nucleus accumbens (Acb) shell is highly implicated in psychostimulant-evoked locomotor activity and reward, whereas the D1R in the Acb core is more crucial for appetitive instrumental learning. These behavioral effects depend in part on interactions involving glutamatergic N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors, whose essential NR1 subunit has physical associations with the D1R. To determine the relevant sites for D1R activation and interactions involving NMDA receptors, we examined the electron microscopic immunolabeling of D1R and NR1 C-terminal peptides in rat Acb shell and core. In each Acb subdivision, the D1Rs were located principally on extrasynaptic plasma membranes of dendritic shafts and spines and more rarely were associated with cytoplasmic endomembranes. Many D1R-labeled somata and dendrites also contained NR1 immunoreactivity. In comparison with D1R, NR1 immunoreactivity was more often seen in the cytoplasm and near asymmetric synapses on somatodendritic profiles. In these profiles, notable overlapping distributions of D1R and NR1 occurred near endomembranes. The exclusively D1R- or D1R- and NR1-containing dendrites were most prevalent in the Acb shell, but were also present in the Acb core. In each region, NR1 was also detected in axon terminals without D1R, which formed excitatory-type synapses with D1R-labeled dendrites. These results provide ultrastructural evidence that D1Rs in the Acb have subcellular distributions supporting, 1) intracellular cotrafficking with NR1 and 2) modulation of the postsynaptic excitability in spiny neurons affected by presynaptic NMDA receptor activation. The region-specific differences in receptor distributions suggest a major, but not exclusive, involvement of Acb D1R in reward-related processing.
Copyright 2005 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Preferential relocation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor NR1 subunit in nucleus accumbens neurons that contain dopamine D1 receptors in rats showing an apomorphine-induced sensorimotor gating deficit.Neuroscience. 2008 Jun 26;154(3):965-77. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.04.009. Epub 2008 Apr 12. Neuroscience. 2008. PMID: 18479834 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine D1 receptors have subcellular distributions conducive to interactions with prodynorphin in the rat nucleus accumbens shell.Synapse. 2006 Jul;60(1):1-19. doi: 10.1002/syn.20273. Synapse. 2006. PMID: 16575853
-
Dendritic distributions of dopamine D1 receptors in the rat nucleus accumbens are synergistically affected by startle-evoking auditory stimulation and apomorphine.Neuroscience. 2007 Jun 8;146(4):1593-605. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.04.005. Epub 2007 May 9. Neuroscience. 2007. PMID: 17490822 Free PMC article.
-
Deletion of the NMDA-NR1 receptor subunit gene in the mouse nucleus accumbens attenuates apomorphine-induced dopamine D1 receptor trafficking and acoustic startle behavior.Synapse. 2013 Jun;67(6):265-79. doi: 10.1002/syn.21637. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Synapse. 2013. PMID: 23345061 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic administration of morphine is associated with a decrease in surface AMPA GluR1 receptor subunit in dopamine D1 receptor expressing neurons in the shell and non-D1 receptor expressing neurons in the core of the rat nucleus accumbens.Exp Neurol. 2008 Apr;210(2):750-61. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2008.01.012. Epub 2008 Jan 26. Exp Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18294632 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Cocaine withdrawal-induced trafficking of delta-opioid receptors in rat nucleus accumbens.Brain Res. 2008 May 19;1210:92-102. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2008.02.105. Epub 2008 Mar 15. Brain Res. 2008. PMID: 18417105 Free PMC article.
-
Direct and indirect interactions of the dopamine D₃ receptor with glutamate pathways: implications for the treatment of schizophrenia.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2013 Feb;386(2):107-24. doi: 10.1007/s00210-012-0797-0. Epub 2012 Sep 22. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23001156 Free PMC article.
-
Limbic and cortical information processing in the nucleus accumbens.Trends Neurosci. 2008 Nov;31(11):552-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2008.08.002. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Trends Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18786735 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Contribution of early environmental stress to alcoholism vulnerability.Alcohol. 2009 Nov;43(7):547-54. doi: 10.1016/j.alcohol.2009.09.029. Alcohol. 2009. PMID: 19913199 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mu-opioid and corticotropin-releasing-factor receptors show largely postsynaptic co-expression, and separate presynaptic distributions, in the mouse central amygdala and bed nucleus of the stria terminalis.Neuroscience. 2009 Mar 17;159(2):526-39. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.12.061. Epub 2009 Jan 8. Neuroscience. 2009. PMID: 19166913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adriani W, Felici A, Sargolini F, Roullet P, Usiello A, Oliverio A, Mele A. N-methyl-D-aspartate and dopamine receptor involvement in the modulation of locomotor activity and memory processes. Exp Brain Res. 1998;123:52–59. - PubMed
-
- Anderson SM, Bari AA, Pierce RC. Administration of the D1-like dopamine receptor antagonist SCH-23390 into the medial nucleus accumbens shell attenuates cocaine priming-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2003;168:132–138. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin AE, Sadeghian K, Holahan MR, Kelley AE. Appetitive instrumental learning is impaired by inhibition of cAMP-dependent protein kinase within the nucleus accumbens. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2002;77:44–62. - PubMed
-
- Brady AE, Limbird LE. G protein-coupled receptor interacting proteins: emerging roles in localization and signal transduction. Cell Signal. 2002;14:297–309. - PubMed
-
- Breukel AI, Besselsen E, Lopes da Silva FH, Ghijsen WE. A presynaptic N-methyl-D-aspartate autoreceptor in rat hippocampus modulating amino acid release from a cytoplasmic pool. Eur J Neurosci. 1998;10:106–114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

