Potential impact of antiviral drug use during influenza pandemic
- PMID: 16229762
- PMCID: PMC3371825
- DOI: 10.3201/eid1209.041344
Potential impact of antiviral drug use during influenza pandemic
Abstract
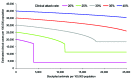
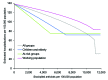
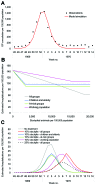
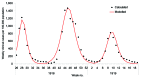
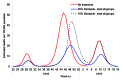
The recent spread of highly pathogenic strains of avian influenza has highlighted the threat posed by pandemic influenza. In the early phases of a pandemic, the only treatment available would be neuraminidase inhibitors, which many countries are considering stockpiling for pandemic use. We estimate the effect on hospitalization rates of using different antiviral stockpile sizes to treat infection. We estimate that stockpiles that cover 20%-25% of the population would be sufficient to treat most of the clinical cases and could lead to 50% to 77% reductions in hospitalizations. Substantial reductions in hospitalization could be achieved with smaller antiviral stockpiles if drugs are reserved for persons at high risk.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Influenza pandemic plan. The role of WHO and guidelines for national and regional planning. Geneva: The Organization; 1999.
-
- UK Department of Health. UK pandemic influenza contingency plan. March 2005. [cited 2005 Mar 1]. Available from http://www.dh.gov.uk/assetRoot/04/10/44/37/04104437.pdf
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
