An expanding family of archaeal transcriptional activators
- PMID: 16230629
- PMCID: PMC1266154
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0508043102
An expanding family of archaeal transcriptional activators
Abstract
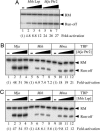
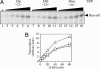
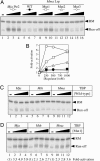
Transcriptional regulation in the archaea involves a mosaic of DNA-binding proteins frequently (although not exclusively) of bacterial type, modulating a eukaryal-type core transcription apparatus. Methanocaldococcus jannaschii (Mja) Ptr2, a homologue of the Lrp/AsnC family of bacterial transcription regulators that are among the most widely disseminated archaeal DNA-binding proteins, has been shown to activate transcription by its conjugate hyperthermophilic RNA polymerase. Here, two in vitro systems have been exploited to show that Ptr2 and a Lrp homologue from the thermophile Methanothermococcus thermolithotrophicus (Mth) activate transcription over a approximately 40 degrees C range, in conjunction with their cognate TATA-binding proteins (TBPs) and with heterologous TBPs. A closely related homologue from the mesophile Methanococcus maripaludis (Mma) is nearly inert as a transcriptional activator, but a cluster of mutations that converts a surface patch of Mma Lrp to identity with Ptr2 confers transcriptional activity. Mja, Mth, and Mma TBPs are interchangeable for basal transcription, but their ability to support Lrp-mediated transcriptional activation varies widely, with Mja TBP the most active and Mth TBP the least active partner. The implications of this finding for understanding the roles of TBP paralogues in supporting the gene-regulatory repertoires of archaeal genomes are briefly noted.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of archaeal transcription by recruitment of the TATA-binding protein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 Apr 29;100(9):5097-102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0837150100. Epub 2003 Apr 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003. PMID: 12692306 Free PMC article.
-
Hybrid Ptr2-like activators of archaeal transcription.Mol Microbiol. 2009 Nov;74(3):582-93. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2009.06884.x. Epub 2009 Sep 22. Mol Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19775246
-
A thermostable platform for transcriptional regulation: the DNA-binding properties of two Lrp homologs from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Methanococcus jannaschii.EMBO J. 2001 Jan 15;20(1-2):146-56. doi: 10.1093/emboj/20.1.146. EMBO J. 2001. PMID: 11226165 Free PMC article.
-
Archaeal transcription and its regulators.Mol Microbiol. 2005 Jun;56(6):1397-407. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2005.04627.x. Mol Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 15916593 Review.
-
Feast/famine regulatory proteins (FFRPs): Escherichia coli Lrp, AsnC and related archaeal transcription factors.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2006 Jan;30(1):89-108. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2005.00005.x. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16438681 Review.
Cited by
-
TBP domain symmetry in basal and activated archaeal transcription.Mol Microbiol. 2009 Jan;71(1):123-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2008.06512.x. Epub 2008 Nov 4. Mol Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19007415 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic and transcriptomic analysis of transcription factor genes in the model halophilic Archaeon: coordinate action of TbpD and TfbA.BMC Genet. 2007 Sep 24;8:61. doi: 10.1186/1471-2156-8-61. BMC Genet. 2007. PMID: 17892563 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of context dependent regulation by expansion of feast/famine regulatory proteins.BMC Syst Biol. 2014 Nov 14;8:122. doi: 10.1186/s12918-014-0122-2. BMC Syst Biol. 2014. PMID: 25394904 Free PMC article.
-
A novel archaeal regulatory protein, Sta1, activates transcription from viral promoters.Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(17):4837-45. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl502. Epub 2006 Sep 14. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006. PMID: 16973899 Free PMC article.
-
Early Response of Sulfolobus acidocaldarius to Nutrient Limitation.Front Microbiol. 2019 Jan 10;9:3201. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.03201. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30687244 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

