BODIPY-conjugated neuropeptide Y ligands: new fluorescent tools to tag Y1, Y2, Y4 and Y5 receptor subtypes
- PMID: 16231000
- PMCID: PMC1751241
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706425
BODIPY-conjugated neuropeptide Y ligands: new fluorescent tools to tag Y1, Y2, Y4 and Y5 receptor subtypes
Abstract
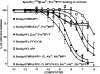
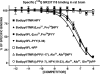
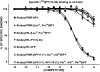
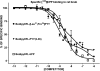
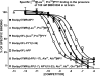
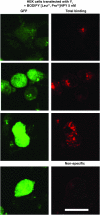
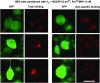
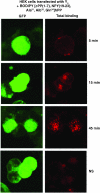
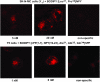
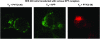
N-terminal labelled fluorescent BODIPY-NPY peptide analogues were tested in Y1, Y2, Y4 and Y5 receptor-binding assays performed in rat brain membrane preparations and HEK293 cells expressing the rat Y1, Y2, Y4 and Y5 receptors. BODIPY TMR/FL-[Leu31, Pro34]NPY/PYY were able to compete for specific [125][Leu31, Pro34]PYY-binding sites with an affinity similar to that observed for the native peptide at the Y1 (Ki=1-6 nM), Y2 (Ki>1000 nM), Y4 (Ki=10 nM) and Y5 (Ki=1-4 nM) receptor subtypes. BODIPY FL-PYY(3-36) was able to compete for specific Y2 (Ki=10 nM) and Y5 (Ki=30 nM) binding sites, but had almost no affinity in Y1 and Y4 assays. BODIPY FL-hPP was able to compete with high affinity (Ki; 1 and 15 nM) only in Y4 and Y5 receptor-binding assays. BODIPY TMR-[cPP(1-7), NPY(19-23), Ala31, Aib32, Gln34]hPP and BODIPY TMR-[hPP(1-17), Ala31, Aib32]NPY were potent competitors only on specific Y5-binding sites (Ki=0.1-0.6 nM). As expected, these fluorescent peptides inhibited forskolin-induced cAMP accumulation, demonstrating that they retained their agonist properties. When tested in confocal microscopy imaging, fluorescent Y1 and Y5 agonists internalized in a time-dependent manner in Y1 and Y5 transfected cells, respectively. These results demonstrate that BODIPY-conjugated NPY analogues retain their selectivity, affinity and agonist properties for the Y1, Y2, Y4 and Y5 receptor subtypes, respectively. Thus, they represent novel tools to study and visualize NPY receptors in living cells.
Figures
References
-
- ARTTAMANGKUL S., ALVAREZ-MAUBECIN V., THOMAS G., WILLIAMS J.T., GRANDY D.K. Binding and internalization of fluorescent opioid peptide conjugates in living cells. Mol. Pharmacol. 2000;58:1570–1580. - PubMed
-
- BARD J.A., WALKER M.W., BRANCHEK T.A., WEINSHANK R.L. Cloning and functional expression of a human Y4 subtype receptor for pancreatic polypeptide, neuropeptide Y, and peptide YY. J. Biol. Chem. 1995;270:26762–26765. - PubMed
-
- BECK-SICKINGER A.G., WIELAND H.A., WITTNEBEN H., WILLIM K.D., RUDOLF K., JUNG G. Complete L-alanine scan of neuropeptide Y reveals ligands binding to Y1 and Y2 receptors with distinguished conformations. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994;225:947–958. - PubMed
-
- BERGLUND M.M., HIPSKIND P.A., GEHLERT D.R. Recent developments in our understanding of the physiological role of PP-fold peptide receptor subtypes. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood.). 2003a;228:217–244. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

