The potential interactions between polyunsaturated fatty acids and colonic inflammatory processes
- PMID: 16232207
- PMCID: PMC1809520
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.2005.02851.x
The potential interactions between polyunsaturated fatty acids and colonic inflammatory processes
Abstract
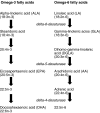
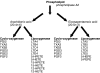
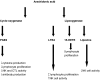
n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are recognized as having an anti-inflammatory effect, which is initiated and propagated via a number of mechanisms involving the cells of the immune system. These include: eicosanoid profiles, membrane fluidity and lipid rafts, signal transduction, gene expression and antigen presentation. The wide-range of mechanisms of action of n-3 PUFAs offer a number of potential therapeutic tools with which to treat inflammatory diseases. In this review we discuss the molecular, animal model and clinical evidence for manipulation of the immune profile by n-3 PUFAs with respect to inflammatory bowel disease. In addition to providing a potential therapy for inflammatory bowel disease there is also recent evidence that abnormalities in fatty acid profiles, both in the plasma phospholipid membrane and in perinodal adipose tissue, may be a key component in the multi-factorial aetiology of inflammatory bowel disease. Such abnormalities are likely to be the result of a genetic susceptibility to the changing ratios of n-3 : n-6 fatty acids in the western diet. Evidence that the fatty acid components of perinodal adipose are fuelling the pro- or anti-inflammatory bias of the immune response is also reviewed.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Modulation of pro-inflammatory cytokine biology by unsaturated fatty acids.Z Ernahrungswiss. 1998;37 Suppl 1:57-65. Z Ernahrungswiss. 1998. PMID: 9558730 Review.
-
Immunomodulation by polyunsaturated fatty acids: mechanisms and effects.Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2003 Dec;132(4):310-21. doi: 10.1159/000074898. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2003. PMID: 14707462 Review.
-
Effects of altering dietary fatty acid composition on prostaglandin synthesis and fertility.Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1999 Nov;61(5):275-87. doi: 10.1054/plef.1999.0101. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids. 1999. PMID: 10670689 Review.
-
Potential of magnetic resonance spectroscopy in assessing the effect of fatty acids on inflammatory bowel disease in an animal model.Lipids. 2010 Sep;45(9):843-54. doi: 10.1007/s11745-010-3455-7. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Lipids. 2010. PMID: 20721632
-
Circulating profiling reveals the effect of a polyunsaturated fatty acid-enriched diet on common microRNAs.J Nutr Biochem. 2015 Oct;26(10):1095-101. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.05.001. Epub 2015 May 30. J Nutr Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26092372
Cited by
-
Novel Anticancer Platinum(IV) Complexes with Adamantylamine: Their Efficiency and Innovative Chemotherapy Strategies Modifying Lipid Metabolism.Met Based Drugs. 2008;2008:417897. doi: 10.1155/2008/417897. Met Based Drugs. 2008. PMID: 18414587 Free PMC article.
-
Perinodal adipose tissue and mesenteric lymph node activation during reactivated TNBS-colitis in rats.Dig Dis Sci. 2011 Sep;56(9):2545-52. doi: 10.1007/s10620-011-1644-8. Epub 2011 Mar 6. Dig Dis Sci. 2011. PMID: 21380759
-
Heterologous production of dihomo-gamma-linolenic acid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007 Nov;73(21):6965-71. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01008-07. Epub 2007 Sep 14. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17873077 Free PMC article.
-
Current view of the immunopathogenesis in inflammatory bowel disease and its implications for therapy.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Apr 7;14(13):1972-80. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.1972. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18395894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyunsaturated fatty acids: From diet to binding to ppars and other nuclear receptors.Genes Nutr. 2006 Jun;1(2):95-106. doi: 10.1007/BF02829951. Genes Nutr. 2006. PMID: 18850203 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sinclair HM. Deficiency of essential fatty acids and atherosclerosis, etcetera. Lancet. 1956;270:381–3. - PubMed
-
- Bang HO. The composition of food consumed by Greenlandic Eskimos. Acta Med Scand. 1976;200:69–73. - PubMed
-
- Kromann N, Green A. Epidemiological studies in the Upernavik district, Greenland. Incidence of some chronic diseases 1950–74. Acta Med. 1980;208:401–6. - PubMed
-
- Shoda R, Matsueda K, Yamato S, Umeda N. Epidemiologic analysis of Crohn disease in Japan: increased dietary intake of n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids and animal protein relates to the increased incidence of Crohn disease in Japan. Am J Clin Nutr. 1996;63:741–5. - PubMed
-
- Sanders TA, Reddy S. Infant brain lipids and diet. Lancet. 1992;340:1093–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical