Surgery for degenerative lumbar spondylosis
- PMID: 16235281
- PMCID: PMC7028012
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001352.pub3
Surgery for degenerative lumbar spondylosis
Abstract
Background: Surgical investigations and interventions account for large health care utilisation and costs, but the scientific evidence for most procedures is still limited.
Objectives: Degenerative conditions affecting the lumbar spine are variously described as lumbar spondylosis or degenerative disc disease (which we regarded as one entity) and may be associated with back pain and associated leg symptoms, instability, spinal stenosis and/or degenerative spondylolisthesis. The objective of this review was to assess current scientific evidence on the effectiveness of surgical interventions for degenerative lumbar spondylosis.
Search strategy: We searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE, PubMed, Spine and ISSLS abstracts, with citation tracking from the retrieved articles. We also corresponded with experts. All data found up to 31 March 2005 are included.
Selection criteria: Randomised (RCTs) or quasi-randomised trials of surgical treatment of lumbar spondylosis.
Data collection and analysis: Two authors assessed trial quality and extracted data from published papers. Additional information was sought from the authors if necessary.
Main results: Thirty-one published RCTs of all forms of surgical treatment for degenerative lumbar spondylosis were identified. The trials varied in quality: only the more recent trials used appropriate methods of randomization, blinding and independent assessment of outcome. Most of the earlier published results were of technical surgical outcomes with some crude ratings of clinical outcome. More of the recent trials also reported patient-centered outcomes of pain or disability, but there is still very little information on occupational outcomes. There was a particular lack of long term outcomes beyond two to three years. Seven heterogeneous trials on spondylolisthesis, spinal stenosis and nerve compression permitted limited conclusions. Two new trials on the effectiveness of fusion showed conflicting results. One showed that fusion gave better clinical outcomes than conventional physiotherapy, while the other showed that fusion was no better than a modern exercise and rehabilitation programme. Eight trials showed that instrumented fusion produced a higher fusion rate (though that needs to be qualified by the difficulty of assessing fusion in the presence of metal-work), but any improvement in clinical outcomes is probably marginal, while there is other evidence that it may be associated with higher complication rates. Three trials with conflicting results did not permit any conclusions about the relative effectiveness of anterior, posterior or circumferential fusion. Preliminary results of two small trials of intra-discal electrotherapy showed conflicting results. Preliminary data from three trials of disc arthroplasty did not permit any firm conclusions.
Authors' conclusions: Limited evidence is now available to support some aspects of surgical practice. Surgeons should be encouraged to perform further RCTs in this field.
Conflict of interest statement
Nil
Figures
































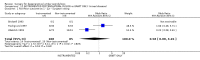
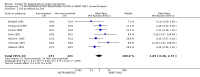








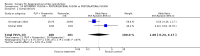









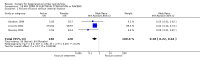





Update of
-
Surgery for degenerative lumbar spondylosis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Apr 18;(2):CD001352. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001352.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Oct 19;(4):CD001352. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001352.pub3. PMID: 15846617 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Amundsen 2000 {published data only}
-
- Amundsen T, Weber H, Nordal HJ, Magnaes B, Abdelnoor M, Lilleas F. Lumbar spinal stenosis; conservative or surgical management? A prospective 10‐year study. Spine 2000;11:1424‐36. - PubMed
Barendse 2001 {published data only}
-
- Barendse GAM, Berg SGM, Kessels AHF, Weber WEJ, Kleef M. Randomized controlled trial of percutaneous intradiscal radiofrequency thermocoagulation for chronic discogenic back pain. Spine 2001;26:287‐92. - PubMed
Bridwell 1993 {published data only}
-
- Bridwell KH, Sedgewick TA, O'Brien MF, Lenke LG, Baldus C. The role of fusion and instrumentation in the treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. J Spinal Disord 1993;6(6):461‐72. - PubMed
Brox 2003 {unpublished data only}
-
- Brox JI, Sorensen R, Friis A, Indahl A, Keller A, Reikeras O, et al. Randomised clinical trial of lumbar instrumented fusion and cognitive intervention and exercises of patients with chronic low back pain and disc degeneration. Proceedings of the International Society for Study of the Lumbar Spine. 2003. - PubMed
-
- Brox JI, Sorensen R, Friis A, Nygaard O, Indahl A, Keller A, et al. Randomized clinical trial of lumbar instrumented fusion and cognitive intervention and exercises in patients with chronic low back pain and disc degeneration. Spine 2003;28(17):1913‐21. - PubMed
Brox 2004 {published data only}
-
- Keller A, Brox JI, Gunderson R, Holm I, Friis A, Reikeras O. Trunk muscle strength, cross‐sectional area and density in patients with chronic low back pain randomized to lumbar fusion or cognitive intervention and exercises. Spine 2004;29(1):3‐8. - PubMed
Carragee 1997 {published data only}
-
- Carragee EJ. Single‐level posterolateral arthrodesis, with or without posterior decompression, for the treatment of isthmic spondylolisthesis in adults. A prospective, randomised study. J Bone Joint Surg 1997;79‐A:1175‐80. - PubMed
Christensen 2002 {published data only}
-
- Bunger C, Eiskjaer S, Hansen ES, Thomsen K, Hoy K, Helmig P, et al. Controversies in lumbar spine fusion ‐ the role of pedicle screw fixation and 360º fusion ‐ randomized prospective studies. Acta Orthop Scand. 1998; Vol. 69:26.
-
- Bunger C, Hansen ES, Hoy K, Neumann P, Niedermann B, Lindblad BE, et al. Lumbar spine fusion. A randomized prospective study of circumferential fusion with the ALIF Brantigan cage versus posterolateral fusion with titanium CDI. Proceedings of the British Scoliosis Society. 2001.
-
- Christensen FB, Hansen ES, Eiskjaer SP, Hoy K, Helmig P, Neumann P, et al. Circumferential lumbar spinal fusion with ALIF Brantigan cage versus posterolateral fusion with titanium CD‐Horizon: a prospective, randomized, clinical study of 146 patients. Spine 2002;27(23):2674‐83. - PubMed
Delamarter 2003 {published data only}
-
- Bae H, Pradhan B, Kanim L, Lam L, Kamrava E, Delamarter R. Clinical results after lumbar total disc replacement: A 2 to 3 year report from the United States clinical trial for the ProDisc‐II prosthesis. Proceedings of the International Society for the Study of the Lumbar Spine. 2005:27.
-
- Delamarter RB, Fribourg DM, Kanim LE, Bae H. ProDisc artificial total lumbar disc replacement: introduction and early results from the United States clinical trial. Spine 2003;28(20S):S167‐75. - PubMed
Fischgrund 1997 {published data only}
-
- Fischgrund J, McKay M, Herkowitz H, Brower R, Montgomery D, Kurz L. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: A prospective, randomized study, comparing decompression and fusion with and without posterior pedicular instrumentation. Orth Trans 1997;21:158.
-
- Fischgrund JS, Mackay M, Herkowitz HN, Brower R, Montgomery DM, Kurz LT. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis: A prospective, randomized study comparing decompressive laminectomy and arthrodesis with and without spinal instrumentation. Spine 1997;22:2807‐12. - PubMed
France 1999 {published data only}
-
- France JC, Yaszemski MJ, Lauerman WC, Cain JE, Glover JM, Lawson KJ, et al. A randomized prospective study of posterolateral lumbar fusion: Outcomes with and without pedicle screw instrumentation. Orthop Trans. 1997; Vol. 21:157. - PubMed
-
- France JC, Yaszemski MJ, Lauerman WC, Cain JE, Glover JM, Lawson KJ, et al. A randomized prospective study of posterolateral lumbar fusion: Outcomes with and without pedicle screw instrumentation. Spine 1999;24:553‐60. - PubMed
Freeman 2003 {published data only}
-
- Freeman BJC, Fraser RD, Cain CMJ, Hall DJ. A randomised double‐blind controlled efficacy study: intradiscal electrothermal therapy (IDET) versus placebo. J Bone Joint Surg. 2003; Vol. 85‐B, issue Supp III:280.
-
- Freeman BJC, Fraser RD, Cain CMJ, Hall DJ. A randomized double‐blind controlled efficacy study: Intradiscal electrothermal therapy (IDET) versus placebo. Proceedings of the International Society for Study of the Lumbar Spine. 2003:Abstract 11.
Fritzell 2001 {published data only}
-
- Fritzell P, Hagg O, Jonsson D, Nordwall A, the Swedish Lumbar Spine Study Group. Cost‐effectiveness of lumbar fusion and nonsurgical treatment for chronic low back pain in the Swedish Lumbar Spine Study: A multicenter, randomized, controlled trial from the Swedish Lumbar Spine Study Group. Spine 2004;29(4):421‐34. - PubMed
-
- Fritzell P, Hagg O, Nordwall A, the Swedish Lumbar Spine Group. Complications in lumbar fusion surgery for chronic low back pain: comparison of three surgical techniques used in a prospective randomized study. A report from the Swedish Lumbar Spine Study Group. Eur Spine J 2003;12(2):178‐89. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fritzell P, Hagg O, Wessberg P, Nordwall A. 2001 Volvo award winner in clinical studies: Lumbar fusion versus nonsurgical treatment for chronic low back pain: A multicentre randomized controlled trial from the Swedish Lumbar Spine Study Group. Spine 2001;26:2521‐34. - PubMed
Goodwin 1999 {published data only}
-
- Goodwin CB, Brighton CT, Guyer RD, Johnson JR, Light KI, Yuan HA. A double‐blind study of capacitively coupled electrical stimulation as an adjunct to lumbar spinal fusions. Spine 1999;24(13):1349‐57. - PubMed
Grob 1995 {published data only}
-
- Grob D, Humke T, Dvorak J. Degenerative lumbar spinal stenosis. Decompression with and without arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1995;77(7):1036‐41. - PubMed
Herkowitz 1991 {published data only}
-
- Herkowitz HN, Kurz LT. Degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis with spinal stenosis. A prospective study comparing decompression with decompression and intertransverse process arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1991;73‐A(6):802‐8. - PubMed
Jenis 2000 {published data only}
-
- Jenis LG, An HS, Stein R, Young B. Prospective comparison of the effect of direct current electrical stimulation and pulsed electromagnetic fields on instrumented posterolateral lumbar arthrodesis. Journal of Spinal Disorders 2000;13(4):290‐6. - PubMed
Kitchel 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kitchel SH, Matteri RE. Prospective randomized evaluation of PLIF in degenerative spondylolisthesis patients over 60 years old. The Spine Journal 2002;2(2 Suppl):21S.
Linovitz 2002 {published data only}
-
- Linovitz RJ, Pathria M, Bernhardt M, Green D, Law MD, McGuire RA, et al. Combined magnetic fields accelerate and increase spine fusion. A double‐blind, randomized, placebo controlled study. Spine 2002;27:1383‐9. - PubMed
Madan 2003 {published data only}
McAfee 2003 {published data only}
-
- Geisler FH, Blumenthal SL, Guyer RD, McAfee PC, Regan JJ, Johnson JP, et al. Neurological complications of lumbar artificial disc replacement and comparison of clinical results with those related to lumbar arthrodesis in the literature: Results of a multicenter, prospective, randomized investigational device exemption study of Charite intervertebral disc. J Neurosurg Spine 2004;1:143‐54. - PubMed
-
- Holt R, Jajd M, Isaza J, Blumnethal S, McAfee P, Guyer R, et al. Complications of lumbar artificial disc replacement vs fusion: Results from the randomized, multicenter FDA IDE study of the Charite artificial disc. Proceedings of the International Society for the Study of the Lumbar Spine.. 2005:31.
-
- McAfee PC, Fedder IL, Saiedy S, Shucosky EM, Cunningham B. Experimental design of total disk replacement ‐ experience with a prospective randomized study of the SB Charite. Spine 2003;28(20S):S153‐62. - PubMed
-
- Whitaker C, Hochschuler S, Ohnmeiss D, Zigler J, Guyer R, Sachs B, et al. Proceedings of the International Society for the Study of the Lumbar Spine. 2005:68.
McGuire 1993 {published data only}
-
- McGuire RA, Amundson GM. The use of primary internal fixation in spondylolisthesis. Spine 1993;18(12):1662‐72. - PubMed
Moller 2000 {published data only}
-
- Moller H, Hedlund R. [Surgery versus conservative treatment in adult isthmic spondylolisthesis. A prospective randomized study]. Thesis: Karolinska Institute. Stockholm: Kongl Carolinska Medico Chirurgiska Institute, 1999. [ISBN 91‐628‐3834‐2]
-
- Moller H, Hedlund R. Surgery versus conservative management in adult isthmic spondylolisthesis. Spine 2000;25(13):1711‐5. - PubMed
-
- Moller H, Hedlund R. Surgery vs. conservative treatment in adult spondylolisthesis ‐ a prospective randomized study. Acta Orthop Scand. 1998; Vol. 69, issue Suppl. 280:13.
-
- Moller H, Hedlund R. Surgery vs. conservative treatment in adult spondylolisthesis. A prospective randomised study. Orthop Trans. 1996; Vol. 20, issue 2:390.
Mooney 1990 {published data only}
-
- Mooney V. A randomized double‐blind prospective study of the efficacy of pulsed electromagnetic fields for interbody lumbar fusions. Spine 1990;15(7):708‐12. - PubMed
Pauza 2004 {published data only}
-
- Pauza K, Howell S, Dreyfuss P, Peloza J, Park K. A randomized, double‐blind, placebo controlled trial evaluating the efficacy of intradiscal electrothermal anuloplasty (IDET) for the treatment of chronic discogenic low back pain: 6‐month outcomes. Proceedings of the International Spinal Injections Society. 2002.
-
- Pauza KJ, Howell S, Dreyfuss P, Peloza JH, Dawson K, Bogduk N. A randomized, placebo‐controlled trail of intradiscal electrotermal therapy for the treatment of discogenic low back pain. Spine Journal 2004;4(1):27‐35. - PubMed
Postacchini 1993 {published data only}
-
- Postacchini F, Cinotti G, Perugia D, Gumina S. The surgical treatment of central lumbar stenosis. J Bone Joint Surg 1993;75‐B:386‐92. - PubMed
Sasso 2004 {published data only}
-
- Sasso RC, Kitchel SH, Dawson EG. A prospective, randomized controlled clinical trial of anterior lumbar interbody fusion using a titanium cylindrical threaded fusion device. Spine 2004;29(2):113‐22. - PubMed
Schofferman 2001 {published data only}
-
- Schofferman J, Slosar P, Reynolds J, Goldthwaite N, Koestler M. A prospective randomized comparison of 270º fusions to 360º fusions (circumferential fusions). Spine (electronic) 2001;26(10):E207‐12. - PubMed
Thomsen 1997 {published data only}
-
- Christensen FB, Hansen ES, Laursen M, Thomsen K, Bunger CE. Long‐term functional outcome of pedicle screw instrumentation as a support for posterolateral spinal fusion. Randomized clinical study with a 5‐year follow‐up. Spine 2002;27(12):1269‐77. - PubMed
-
- Korsgaard M, Christensen FB, Thomsen K, Hansen ES, Bonger C. The effect of pedicle screw instrumentation on lordosis in lumbar spinal fusion. J Bone Joint Surg. 1999; Vol. 81‐B, issue Suppl. II:188.
-
- Thomsen K, Christensen FB, Eiskjaer SP, Hansen ES, Fruensgaard S, Bunger CE. The effect of pedicle screw instrumentation on functional outcome and fusion rates in posterolateral lumbar spinal fusion. A prospective randomized clinical study. Spine 1997;22:2813‐22. - PubMed
-
- Thomsen K, Eiskjaer S, Hansen ES, Fruensgaard S, Christensen FB, Bunger C. Lumbar posterolateral fusion ‐ the consequences of pedicle screw instrumentation. Acta Orthop Scand. 1996; Vol. 67:48.
Zdeblick 1993 {published data only}
-
- Zdeblick TA. A prospective, randomized study of lumbar fusion. Preliminary results [see comments]. Spine 1993;18(8):983‐91. - PubMed
-
- Zdeblick TA, Ulschmid S. An outcomes and cost analysis of pedicle screw fusions. Orthop Trans 1996;20:362‐3.
Zigler 2003 {published data only}
-
- Whitaker C, Hochschuler SH, Ohnmeiss DD, Zigler JE, Guyer RD, Sachs BL, et al. Return to work following total disc replacement vs. fusion: A prospective randomized, comparison study. Proceedings of the International Society for Surgery of the Lumbar Spine. 2005:68.
-
- Zigler JE, Burd TA, Vialle EN, Sachs BL, Rashbaum RF, Ohnmeiss DD. Lumbar spine arthroplasty. Early results using the ProDisc II: A prospective randomized trial of arthroplasty versus fusion. Journal of Spinal Disorders 2003;16(4):352‐61. - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Boden 2002 {published data only}
-
- Boden SD, Kang J, Sandhu H, Heller JG. Use of recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein‐2 to achieve posterolateral lumbar spine fusion in humans. Spine 2002;27:2662‐73. - PubMed
Christensen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Christensen FB, Laurberg I, Bunger CE. Importance of the back‐cafe concept to rehabilitation after lumbar spinal fusion: A randomized clinical study with a 2‐year follow‐up. Spine 2003;28(23):2561‐9. - PubMed
Emery 1995 {published data only}
-
- Emery SE, Stephens GC, Bolesta MJ. Lumbar fusion with and without instrumentation: A prospective study. [Abstract] Orthop Trans 1995;19(2):362.
Ercelen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Ercelen O, Bulutcu E, Oktenoglu T, Sasani M, Bozkus H, Saryoglu AC, et al. Radiofrequency lesioning using two different time modalities for the treatment of lumbar discogenic pain: A randomized trial. Spine 2003;28(17):1922‐7. - PubMed
Gibson S 2002 {published data only}
-
- Gibson S, McLeod I, Wardlaw D, Urbaniak S. Allograft versus autograft in instrumented posterolateral lumbar spinal fusion: A randomized control trial. Spine 2002;27(15):1599‐1603. - PubMed
Johnsson 2002 {published data only}
-
- Johnsson R, Stromqvist B, Aspenberg P. Randomized radiostereometric study comparing osteogenic protein‐1 (BMP‐7) and autograft bone in human noninstrumented posterolateral lumbar fusion. Spine 2002;27:2654‐61. - PubMed
Khot 2004 {published data only}
-
- Khot A, Bowditch M, Powell J, Sharp D. The use of intradiscal steroid therapy for lumbar spinal discogenic pain: a randomized controlled trial. Spine 2004;29:833‐6. - PubMed
Korovessis 2003 {published data only}
-
- Korovessis P, Papazisis Z, Koureas G, Zacharatos S. Rigid vs semirigid and dynamic instrumentation for stabilization the degenerated lumbosacral spine associated with spinal stenosis. Eur Spine J. 2003; Vol. 12, issue Suppl 1:S6‐7.
Laine 2000 {published data only}
McAfee 2002 {published data only}
-
- McAfee PC, Lee GA, Fedder IL, Cunningham BW. Anterior BAK instrumentation and fusion: complete versus partial discectomy. Clin Orthop 2002, (394):55‐63. - PubMed
Moore 1995 {published data only}
-
- Moore KR, Schlegel JD. Early outcome of prospective data for the treatment of degenerative spondylolisthesis comparing in situ fusion versus pedicle screw instrumentation and fusion. Orthop Trans. 1995; Vol. 19:62.
North 1995 {published data only}
-
- North RB, Kidd DH, Piantadosi S. Spinal cord stimulation versus reoperation for failed back surgery syndrome: A prospective randomized study design. Acta Neurochir 1995;64:106‐8. - PubMed
Rogozinski 1995 {published data only}
-
- Rogozinski A, Rogozinski C. Efficacy of implanted bone growth stimulation in instrumented lumbosacral spinal fusion. Orthop trans 1995;19:362. - PubMed
Sachs 2002 {published data only}
-
- Sachs B, McVoy J, Miller B, Ohnmeiss D. A prospective, randomized comparison of laparoscopic to open anterior lumbar interbody fusion with cages. Proceedings of the Meeting of the Americas II, New York. 2002.
Sanden 2002 {published data only}
-
- Sanden B, Olerud C, Petren‐Mallmin MP, Larsson S. Hydroxyapatite coating improves fixation of pedicle screws: A clinical study. J Bone Joint Surg 2002;84‐B:387‐91. - PubMed
Soegaard 2003 {published data only}
-
- Soegaard R, Christensen FB, Laurberg I, Bunger CE. Cost‐effectiveness analysis on different rehabilitation strategies after lumbar spinal fusion ‐ A randomized prospective study. Eur Spine J 2003;12(Suppl 1):S10‐11.
Transfeldt 2001 {published data only}
-
- Transfeldt EE, Burkus JK, Kitchel SH, Watkins R, Balderston RA. A prospective and randomized study assessing the clinical and radiographic outcomes of patients treated with rhBMP‐2 and threaded cortical bone dowels in the lumbar spine. Proceedings of the British Scoliosis Society. 2001.
von Strempel 1997 {published data only}
-
- Strempel AH. Results of dynamic versus rigid instrumentation of the spine. J Bone Joint Surg. 1997; Vol. 79‐B:Supp IV:441.
Zdeblick 1996 {published data only}
-
- Zdeblick TA, Ulschmid S, Dick JC. The surgical treatment of L5‐S1 degenerative disc disease ‐ A prospective randomized study of laparoscopic fusion. Orthop Transactions 1996;20:75.
-
- Zdeblick TA, Ulschmid S, Dick JC. The surgical treatment of L5‐S1 degenerative disc disease ‐ A prospective randomized study of laparoscopic fusion. Orthopaedic Transactions 1996‐7;20:1064‐5.
Zhao 2002 {published data only}
-
- Zhao J, Wang X, Hou T, He S. One versus two BAK fusion cages in posterior lumbar interbody fusion to L4‐L5 degenerative spondylolisthesis. Spine 2002;27:2753‐7. - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Fairbank 2005 {published data only}
-
- Fairbank J, Frost H, Wilson‐MacDonald J, Yu L, Barker K, Collins R and the Spine Stabilisation Group. Randomised controlled trial to compare surgical stabilisation of the lumbar spine with an intensive rehabilitation programme for patients with chronic low back pain: the MRC spine stabilisation trial. BMJ 2005;330:1233‐43. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Rivero‐Arias O, Campbell HE, Gray AM, Fairbank J, Frost H, Wilson‐MacDonald J and the Spine Stabilisation Trial Group. Surgical stabilisation of the spine compared with a programme of intensive rehabilitation for the management of patients with chronic low back pai: cost utility analysis based on a randomised controlled trial. BMJ 2005;330:1239‐43. - PMC - PubMed
Ma 2001 {published data only}
-
- Ma Y, Guo L, Cai X. Posterior interbody fusion or posterolateral fusion for discogenic low back pain. Ahonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 2001;81(20):1253‐5. - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Clarke 2003 {published data only}
-
- A Prospective randomised trial comparing femoral ring allograft versus a titanium cage for circumferential spinal fusion: two year functional and radiological outcome. Ongoing study 2001.
Freeman 2005 {published data only}
Gibson 2003 {published data only}
-
- Gibson JNA, Hallett A. Spinal fusion in patients with single level degenerate disc disease and neural compression ‐ A prospective randomised study. Proceedings of the International Society for Study of the Lumbar Spine. 2003.
Ilharreborde 2005 {published data only}
-
- Ilharreborde B, Olivier E, Rillardon L, Vialle R, Guigui P. Efficiency of total disc replacement arthroplasty in the treatment of chronic low back pain. Proceedings of the International Society for the Study of the Lumbar Spine. 2005:10.
Malmivaara 2003 {published data only}
-
- Malmivaara A, Slatis P, Heliovaara M, Sainio P, Kinnunen H, Kankare J, et al. Operative treatment for moderately severe lumbar spinal stenosis: a randomized controlled trial. Proceedings of the International Society for Study of the Lumbar Spine. 2003.
Whitaker 2005 {published data only}
-
- Whitaker C, Hochschuler S, Ohnmeiss D, Zigler J, Guyer R, Sachs B, et al. Return to work following total disc replacement vs. fusion: A prospective, randomized, comparison study. Proceedings of the International Society for the Study of the Lumbar Spine. 2005:68.
Additional references
Alderson 2003
-
- Alderson P, Green S, Higgins JPT, Editors. The Cochrane Reviewer's Handbook 4.2 [updated December 2003]. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. Chichester, UK: John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2004, issue 1:Appendix 5c.
Blumenthal 1993
-
- Blumenthal SL, Gill K. Can lumbar spine radiographs accurately determine fusion in post‐operative patients? Correlation of routine radiographs with a second surgical look at lumbar fusion. Spine 1993;19:1186‐9. - PubMed
Bono 2004
-
- Bono CM, Lee CK. Critical analysis of trends in fusion for degenerative disc disease over the past 20 years: influence of technique on fusion rate and clinical outcome. Spine 2004;29(4):455‐63. - PubMed
Cha 2003
-
- Cha CW, Boden SD. Gene therapy applications for spine fusion. Spine 2003;28(15):S74‐84. - PubMed
Ciol 1996
-
- Ciol MA, Deyo RA, Howell E, Krief S. An assessment of surgery for spinal stenosis time trends, geographic variations, complications and reoperations. J Amer Geront Soc 1996;44:285‐90. - PubMed
Deyo 1992
-
- Deyo RA, Cherkin DC, Loeser JD, Bigos SJ, Ciol MA. Morbidity and mortality in association with operations on the lumbar spine. The influence of age, diagnosis and procedure. J Bone Joint Surg 1992;74‐A:536‐43. - PubMed
Deyo 1998
-
- Deyo R, Battie M, Beurskens A, Bombardier C, Croft P, Koes B, et al. Outcome measures for low back pain research: a proposal for standardised use. Spine 1998;23:2003‐13. - PubMed
Goosens 1998
-
- Goosens M, Evers S. Economic evaluation of back pain interventions. In: Nachemson A, Jonsson E editor(s). SBU report on back pain. Stockholm: Swedish Council on Technology Assessment in Health Care, 1998.
Indahl 1995
-
- Indahl A, Velund L, Reikeraas O. Good prognosis for low back pain when left untampered: a randomized clinical trial. Spine 1995;20:473‐7. - PubMed
Kant 1995
-
- Kant AP, Daum WJ, Dean SM, Vehida T. Evaluation of lumbar spine fusion. Plain radiographs versus direct surgical exploration and observation. Spine 1995;20:2313‐7. - PubMed
Keller 2004
-
- Keller A, Brox JI, Gunderson R, Holm IPT, Friis A, Reikeras O. Trunk muscle strength, cross‐sectional area and density in patients with chronic low back pain randomized to lumbar fusion or cognitive intervention and exercises. Spine 2004;29(1):3‐8. - PubMed
Mardjetko 1994
-
- Mardjetko SM, Connolly PJ, Shott S. Degenerative lumbar spondylosis: a meta‐analysis of the literature 1970‐1993. Spine 1994;19:2256S‐65S. - PubMed
Roy‐Camille 1986
-
- Roy‐Camille R, Saillant G, Mazel C. Internal fixation of the lumbar spine with pedicle screw plating. Clin Orthop 1986;203:7‐17. - PubMed
Sandhu 2003
-
- Sandhu HS. Bone morphogenetic proteins and spinal surgery. Spine 2003;28(15):S64‐73. - PubMed
Schulz 1995
-
- Schulz KF, Chalmers I, Hayes RJ, Altman DG. Empirical evidence of bias dimensions of methodological quality associated with estimates of treatment effects in controlled trials. JAMA 1995;273:408‐12. - PubMed
Szpalski 1997
-
- Szpalski M, Gunzburg R. Lumbar segmental instability: fact or fiction?. Proceedings of the IVth Brussels International Spine Symposium. Brussels, 1997.
Turner 1992a
-
- Turner JA, Ersek M, Herron L, Deyo R. Surgery for lumbar spinal stenosis: attempted meta‐analysis of literature 1970‐93. Spine 1992;17:1‐8. - PubMed
Turner 1992b
-
- Turner JA, Ersek M, Herron L, Haselkorn J, Kent D, Ciol MA, et al. Patient outcomes after lumbar spinal fusions. JAMA 1992;268:907‐11. - PubMed
van Tulder 2003
-
- Tulder M, Furlan A, Bombardier C, Bouter L and the Editorial Board of the Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group. Updated method guidelines for systematic reviews in the Cochrane Collaboration Back Review Group. Spine 2003;28:1290‐9. - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Gibson 1999
-
- Gibson JNA, Grant IC, Waddell G. The Cochrane review of surgery for lumbar disc prolapse and degenerative lumbar spondylosis. Spine 1999;24(17):1820‐32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

