Trends in prescribing and utilization of statins and other lipid lowering drugs across Europe 1997-2003
- PMID: 16236045
- PMCID: PMC1884951
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02478.x
Trends in prescribing and utilization of statins and other lipid lowering drugs across Europe 1997-2003
Abstract
Aims: To describe trends in utilization and prescribing of statins and other lipid lowering drugs across Europe from data in routine administrative databases.
Methods: Observational study in EU member states and Norway. Comparison of annual utilization data for lipid lowering agents by class and drug from national administrative databases for reimbursement over the period 1997-2003, measured in DDDs per 1000 inhabitants/day. Prescribed daily doses (PDD) of statins obtained from a commercial database (IMS Health) for 2000 and 2003, and used to calculate numbers of "patient treatment days" (PTD) in each country in each year. Analysis of PTD to explain increased utilization of statins.
Results: Use of lipid lowering agents varied among countries (in 2003, highest in Ireland and Norway, and lowest in Italy), but increased in all countries studied (between 2000 and 2003 by 274% in Ireland and by 56% in France). This increase was entirely due to increases in statin use. Prescribed daily doses of statins increased in all countries for which data was available between 2000 and 2003, but still usually fell below the doses used in the major trials of statins. As a result, the numbers of PTDs increased to a lesser extent than suggested by utilization (e.g. by 192% in Ireland and by 35% in France). One-third of the total rise in utilization was explained by increased PDD, and two-thirds by an increase in numbers of PTDs. Statins dominated the markets in all countries, although fibrates remained strong in France and Belgium (approximately 25% of all lipid lowering agents) and to a lesser extent Germany (10%).
Conclusions: Use of statins across Europe has increased hugely over the study period. Some of the increase in use is due to higher prescribed daily doses, but two-thirds is due to increases in numbers of patient days of treatment, either due to more patients treated or less likely to better compliance.
Figures
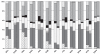
 ), simvastatin (▪), lovastatin (
), simvastatin (▪), lovastatin ( ), pravastatin (
), pravastatin ( ), fluvastatin (▪), atorvastatin (
), fluvastatin (▪), atorvastatin ( ), cerivastatin (
), cerivastatin ( ), rosuvastatin (
), rosuvastatin ( )
)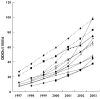
 ), Netherlands (
), Netherlands ( ), Belgium (
), Belgium ( ), Sweden (
), Sweden ( ), Finland (
), Finland ( ), Germany (
), Germany ( ), Spain (
), Spain ( ), UK (
), UK ( ), Austria (
), Austria ( ), Denmark (
), Denmark ( ), Italy (
), Italy ( ), France (
), France ( ), Ireland (
), Ireland ( )
)Comment in
-
Prescribing statins.Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005 Nov;60(5):457-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.2005.02521.x. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 16236034 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- WHO. European Health for All Database. 2003. [4 March 2005]. http://www.euro.who.International/InformationSources/Data/20010827_1 January.
-
- Pignone M, Rihal C, Bazian Ltd. Clinical Evidence. London: BMJ Books; 2003. Secondary prevention of ischaemic cardiac events; pp. 106–8. - PubMed
-
- Walley T, Folino-Gallo P, Schwabe U, Van Ganse E, Stephens P. Comparison of national administrative and commercial databases to monitor expenditure and costs of statins across Europe. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2004;60:503–11. - PubMed
-
- Guidelines Subcommittee. 1999 World Health Organization-International Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of hypertension. J Hypertens. 1999;17:151–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

