Induction of macrophage-derived SLPI by Mycobacterium tuberculosis depends on TLR2 but not MyD88
- PMID: 16236128
- PMCID: PMC1802419
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2005.02238.x
Induction of macrophage-derived SLPI by Mycobacterium tuberculosis depends on TLR2 but not MyD88
Abstract
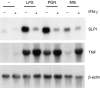
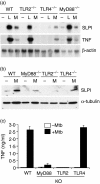
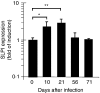
Macrophages respond to Mycobacterium tuberculosis by regulating expression of gene products that initiate a host innate response to this micro-organism. In this study, we report that exposure of murine peritoneal macrophages to heat-killed Mycobacterium tuberculosis (HK-Mtb) led to an increase in secretory leucocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI) gene expression and protein secretion in a time- and dose-dependent manner. HK-Mtb-induced SLPI mRNA expression was sensitive neither to a protein synthesis inhibitor, cycloheximide, nor to an actin polymerization blocker, cytochalasin D. Treatment of macrophages with interferon (IFN)-gamma inhibited HK-Mtb-induced SLPI expression. RAW264.7 cells stably expressing SLPI produced a reduced level of tumour necrosis factor (TNF) in response to HK-Mtb as compared with mock transfectants. Aerosol infection of mice with live M. tuberculosis resulted in an induction of SLPI gene expression in infected lungs. Macrophages from Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-/- or MyD88-/- mice responded to M. tuberculosis similarly to wild-type macrophages by exhibiting increased SLPI expression. In contrast, macrophages from TLR2-/- mice were incapable of inducing SLPI in response to M. tuberculosis. This induction signifies the presence of a TLR2-dependent but MyD88-independent M. tuberculosis signalling pathway, suggesting involvement of adaptor protein(s) other than MyD88 in M. tuberculosis-mediated induction of SLPI.
Figures


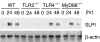

References
-
- Barton GM, Medzhitov R. Toll-like receptor signaling pathways. Science. 2003;300:1524–5. - PubMed
-
- O'Neill LA, Fitzgerald KA, Bowie AG. The Toll-IL-1 receptor adaptor family grows to five members. Trends Immunol. 2003;24:286–90. - PubMed
-
- Modlin RL. Activation of toll-like receptors by microbial lipoproteins: role in host defense. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001;108:S104–6. - PubMed
-
- Horng T, Barton GM, Medzhitov R. TIRAP: an adapter molecule in the Toll signaling pathway. Nat Immunol. 2001;2:835–41. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto M, Sato S, Hemmi H, et al. Essential role for TIRAP in activation of the signalling cascade shared by TLR2 and TLR4. Nature. 2002;420:324–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

