Dysregulation of TGF-beta1 receptor activation leads to abnormal lung development and emphysema-like phenotype in core fucose-deficient mice
- PMID: 16236725
- PMCID: PMC1257418
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0507375102
Dysregulation of TGF-beta1 receptor activation leads to abnormal lung development and emphysema-like phenotype in core fucose-deficient mice
Abstract
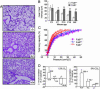
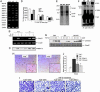
The core fucosylation (alpha1,6-fucosylation) of glycoproteins is widely distributed in mammalian tissues, and is altered under pathological conditions. To investigate physiological functions of the core fucose, we generated alpha1,6-fucosyltransferase (Fut8)-null mice and found that disruption of Fut8 induces severe growth retardation and death during postnatal development. Histopathological analysis revealed that Fut8(-/-) mice showed emphysema-like changes in the lung, verified by a physiological compliance analysis. Biochemical studies indicated that lungs from Fut8(-/-) mice exhibit a marked overexpression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), such as MMP-12 and MMP-13, highly associated with lung-destructive phenotypes, and a down-regulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) proteins such as elastin, as well as retarded alveolar epithelia cell differentiation. These changes should be consistent with a deficiency in TGF-beta1 signaling, a pleiotropic factor that controls ECM homeostasis by down-regulating MMP expression and inducing ECM protein components. In fact, Fut8(-/-) mice have a marked dysregulation of TGF-beta1 receptor activation and signaling, as assessed by TGF-beta1 binding assays and Smad2 phosphorylation analysis. We also show that these TGF-beta1 receptor defects found in Fut8(-/-) cells can be rescued by reintroducing Fut8 into Fut8(-/-) cells. Furthermore, exogenous TGF-beta1 potentially rescued emphysema-like phenotype and concomitantly reduced MMP expression in Fut8(-/-) lung. We propose that the lack of core fucosylation of TGF-beta1 receptors is crucial for a developmental and progressive/destructive emphysema, suggesting that perturbation of this function could underlie certain cases of human emphysema.
Figures

Comment in
-
The search for glycan function: fucosylation of the TGF-beta1 receptor is required for receptor activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005 Nov 1;102(44):15721-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507659102. Epub 2005 Oct 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005. PMID: 16249330 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Lubke, T., Marquardt, T., Etzioni, A., Hartmann, E., von Figura, K. & Korner, C. (2001) Nat. Genet. 28, 73-76. - PubMed
-
- Luhn, K., Wild, M. K., Eckhardt, M., Gerardy-Schahn, R. & Vestweber, D. (2001) Nat. Genet. 28, 69-72. - PubMed
-
- Moloney, D. J., Panin, V. M., Johnston, S. H., Chen, J., Shao, L., Wilson, R., Wang, Y., Stanley, P., Irvine, K. D., Haltiwanger, R. S. & Vogt, T. F. (2000) Nature 406, 369-375. - PubMed
-
- Sturla, L., Rampal, R., Haltiwanger, R. S., Fruscione, F., Etzioni, A. & Tonetti, M. (2003) J. Biol. Chem. 278, 26727-26733. - PubMed
-
- Sturla, L., Fruscione, F., Noda, K., Miyoshi, E., Taniguchi, N., Contini, P. & Tonetti, M. (2005) Glycobiology, in press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

