Chironomus tentans-repressor splicing factor represses SR protein function locally on pre-mRNA exons and is displaced at correct splice sites
- PMID: 16236800
- PMCID: PMC1345644
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e05-04-0339
Chironomus tentans-repressor splicing factor represses SR protein function locally on pre-mRNA exons and is displaced at correct splice sites
Abstract
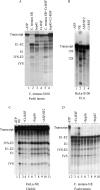
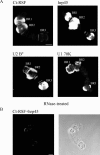
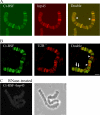
Chironomus tentans-repressor splicing factor (Ct-RSF) represses the activation of splicing by SR proteins in vitro. Ct-RSF colocalizes with the Ser-Arg-rich (SR) protein hrp45 in interchromatin granule clusters and coimmunoprecipitates with hrp45 in nuclear extracts. Ct-RSF and hrp45 can also interact directly in vitro. Ct-RSF and hrp45 are recruited together to transcribing genes and associate with growing pre-mRNAs. Ct-RSF and hrp45 colocalize at a large number of gene loci. Injection of anti-Ct-RSF antibodies into nuclei of living cells blocks association of both Ct-RSF and hrp45 with the growing pre-mRNA, whereas binding of U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particle (snRNP) to the pre-mRNA is unaffected. On the intron-rich Balbiani ring (BR) 3 pre-mRNA, hrp45 as well as U1 and U2 snRNPs bind extensively, whereas relatively little Ct-RSF is present. In contrast, the BR1 and BR2 pre-mRNAs, dominated by exon sequences, bind relatively much Ct-RSF compared with hrp45 and snRNPs. Our data suggest that Ct-RSF represses SR protein function at exons and that the assembly of spliceosomes at authentic splice sites displaces Ct-RSF locally.
Figures






Similar articles
-
A specific SR protein binds preferentially to the secretory protein gene transcripts in salivary glands of Chironomus tentans.Chromosoma. 2006 Dec;115(6):449-58. doi: 10.1007/s00412-006-0073-5. Epub 2006 Jul 21. Chromosoma. 2006. PMID: 16858590
-
A protein of the SR family of splicing factors binds extensively to exonic Balbiani ring pre-mRNA and accompanies the RNA from the gene to the nuclear pore.Genes Dev. 1996 Nov 15;10(22):2881-93. doi: 10.1101/gad.10.22.2881. Genes Dev. 1996. PMID: 8918889
-
Demonstration of a dynamic, transcription-dependent organization of pre-mRNA splicing factors in polytene nuclei.J Cell Biol. 1996 Jun;133(5):929-41. doi: 10.1083/jcb.133.5.929. J Cell Biol. 1996. PMID: 8655585 Free PMC article.
-
Processing of pre-mRNA in polytene nuclei of Chironomus tentans salivary gland cells.Exp Cell Res. 1996 Dec 15;229(2):240-6. doi: 10.1006/excr.1996.0366. Exp Cell Res. 1996. PMID: 8986604 Review.
-
Pre-mRNA splicing in the new millennium.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001 Jun;13(3):302-9. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00212-x. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11343900 Review.
Cited by
-
Specific combinations of SR proteins associate with single pre-messenger RNAs in vivo and contribute different functions.J Cell Biol. 2009 Feb 23;184(4):555-68. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200806156. Epub 2009 Feb 16. J Cell Biol. 2009. PMID: 19221196 Free PMC article.
-
A specific SR protein binds preferentially to the secretory protein gene transcripts in salivary glands of Chironomus tentans.Chromosoma. 2006 Dec;115(6):449-58. doi: 10.1007/s00412-006-0073-5. Epub 2006 Jul 21. Chromosoma. 2006. PMID: 16858590
-
Nucleocytoplasmic mRNP export is an integral part of mRNP biogenesis.Chromosoma. 2011 Feb;120(1):23-38. doi: 10.1007/s00412-010-0298-1. Epub 2010 Nov 16. Chromosoma. 2011. PMID: 21079985 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alzhanova-Ericsson, A. T., Sun, X., Visa, N., Kiseleva, E., Wurtz, T., and Daneholt, B. (1996). A protein of the SR family of splicing factors binds extensively to exonic Balbiani ring pre-mRNA and accompanies the RNA from the gene to the nuclear pore. Genes Dev. 10, 2881–2893. - PubMed
-
- Baurén, G., and Wieslander, L. (1994). Splicing of Balbiani ring 1 pre-mRNA occurs simultaneously with transcription. Cell 76, 183–192. - PubMed
-
- Bentley, D. (2002). The mRNA assembly line: transcription and processing machines in the same factory. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 14, 336 –342. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

