Aldosterone-sensitive repression of ENaCalpha transcription by a histone H3 lysine-79 methyltransferase
- PMID: 16236820
- PMCID: PMC3009459
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpcell.00431.2005
Aldosterone-sensitive repression of ENaCalpha transcription by a histone H3 lysine-79 methyltransferase
Abstract
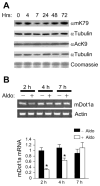
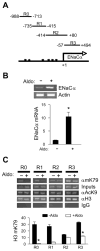
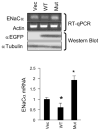
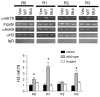
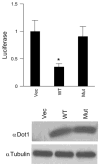
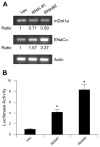
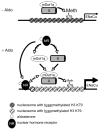
Aldosterone is a major regulator of epithelial Na(+) absorption. One of its principal targets is the epithelial Na(+) channel alpha-subunit (ENaCalpha), principally expressed in the kidney collecting duct, lung, and colon. Models of aldosterone-mediated trans-activation of the ENaCalpha gene have focused primarily on interactions of liganded nuclear receptors with the ENaCalpha gene promoter. Herein, we demonstrate that the murine histone H3 lysine-79 methyltransferase, murine disruptor of telomeric silencing alternative splice variant "a" (mDot1a), is a novel component in the aldosterone signaling network controlling transcription of the ENaCalpha gene. Aldosterone downregulated mDot1a mRNA levels in murine inner medullary collecting ducts cells, which was associated with histone H3 K79 hypomethylation in bulk histones and at specific sites in the ENaCalpha 5'-flanking region, and trans-activation of ENaCalpha. Knockdown of mDot1a by RNA interference increased activity of a stably integrated ENaCalpha promoter-luciferase construct and expression of endogenous ENaCalpha mRNA. Conversely, overexpression of EGFP-tagged mDot1a resulted in hypermethylation of histone H3 K79 at the endogenous ENaCalpha promoter, repression of endogenous ENaCalpha mRNA expression, and decreased activity of the ENaCalpha promoter-luciferase construct. mDot1a-mediated histone H3 K79 hypermethylation and repression of ENaCalpha promoter activity was abolished by mDot1a mutations that eliminate its methyltransferase activity. Collectively, our data identify mDot1a as a novel aldosterone-regulated histone modification enzyme, and, through binding the ENaCalpha promoter and hypermethylating histone H3 K79 associated with the ENaCalpha promoter, a negative regulator of ENaCalpha transcription.
Figures
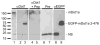
References
-
- Asher C, Wald H, Rossier BC, Garty H. Aldosterone-induced increase in the abundance of Na+ channel subunits. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 1996;271:C605–C611. - PubMed
-
- Boyd C, Naray-Fejes-Toth A. Gene regulation of ENaC subunits by serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase-1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2005;288:F505–F512. - PubMed
-
- Cheung P, Tanner KG, Cheung WL, Sassone-Corsi P, Denu JM, Allis CD. Synergistic coupling of histone H3 phosphorylation and acetylation in response to epidermal growth factor stimulation. Mol Cell. 2000;5:905–915. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

