Diversification of DNA sequences in the symbiotic genome of Rhizobium etli
- PMID: 16237002
- PMCID: PMC1272992
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.21.7185-7192.2005
Diversification of DNA sequences in the symbiotic genome of Rhizobium etli
Abstract
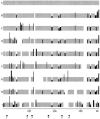
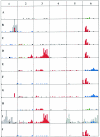
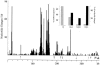
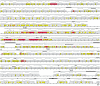
Bacteria of the genus Rhizobium and related genera establish nitrogen-fixing symbioses with the roots of leguminous plants. The genetic elements that participate in the symbiotic process are usually compartmentalized in the genome, either as independent replicons (symbiotic plasmids) or as symbiotic regions or islands in the chromosome. The complete nucleotide sequence of the symbiotic plasmid of Rhizobium etli model strain CFN42, symbiont of the common bean plant, has been reported. To better understand the basis of DNA sequence diversification of this symbiotic compartment, we analyzed the distribution of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in homologous regions from different Rhizobium etli strains. The distribution of polymorphisms is highly asymmetric in each of the different strains, alternating regions containing very few changes with regions harboring an elevated number of substitutions. The regions showing high polymorphism do not correspond with discrete genetic elements and are not the same in the different strains, indicating that they are not hypervariable regions of functional genes. Most interesting, some highly polymorphic regions share exactly the same nucleotide substitutions in more than one strain. Furthermore, in different regions of the symbiotic compartment, different sets of strains share the same substitutions. The data indicate that the majority of nucleotide substitutions are spread in the population by recombination and that the contribution of new mutations to polymorphism is relatively low. We propose that the horizontal transfer of homologous DNA segments among closely related organisms is a major source of genomic diversification.
Figures
References
-
- Achtman, M., G. Morelli, P. Zhu, T. Wirth, I. Diehl, B. Kusecek, A. J. Vogel, D. M. Wagner, C. J. Allender, W. R. Easterday, V. Chenal-Francisque, P. Worsham, N. R. Thomson, J. Parkhill, L. E. Lindler, E. Carniel, and P. Keim. 2004. Microevolution and history of the plague bacillus, Yersinia pestis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:17837-17842. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anderson, R. P., and J. R. Roth. 1977. Tandem genetic duplications in phage and bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 31:473-504. - PubMed
-
- D'hooghe, I., J. Michiels, K. Vlassak, C. Verreth, F. Walkens, and J. Venderleyden. 1995. Structural and functional analysis of the fixLJ genes of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv phaseoli CNPAF512. Mol. Gen. Genet. 249:117-126. - PubMed
-
- Feil, E. J. 2004. Small change: keeping pace with microevolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2:483-495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

