Rhamnolipids modulate swarming motility patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- PMID: 16237018
- PMCID: PMC1273001
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.187.21.7351-7361.2005
Rhamnolipids modulate swarming motility patterns of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Abstract
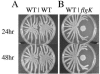
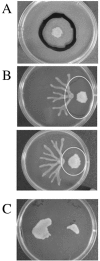
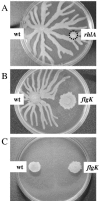
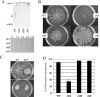
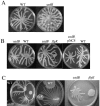
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is capable of twitching, swimming, and swarming motility. The latter form of translocation occurs on semisolid surfaces, requires functional flagella and biosurfactant production, and results in complex motility patterns. From the point of inoculation, bacteria migrate as defined groups, referred to as tendrils, moving in a coordinated manner capable of sensing and responding to other groups of cells. We were able to show that P. aeruginosa produces extracellular factors capable of modulating tendril movement, and genetic analysis revealed that modulation of these movements was dependent on rhamnolipid biosynthesis. An rhlB mutant (deficient in mono- and dirhamnolipid production) and an rhlC mutant (deficient in dirhamnolipid production) exhibited altered swarming patterns characterized by irregularly shaped tendrils. In addition, agar supplemented with rhamnolipid-containing spent supernatant inhibited wild-type (WT) swarming, whereas agar supplemented with spent supernatant from mutants that do not make rhamnolipids had no effect on WT P. aeruginosa swarming. Addition of purified rhamnolipids to swarming medium also inhibited swarming motility of the WT strain. We also show that a sadB mutant does not sense and/or respond to other groups of swarming cells and this mutant was capable of swarming on media supplemented with rhamnolipid-containing spent supernatant or purified rhamnolipids. The abilities to produce and respond to rhamnolipids in the context of group behavior are discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Ausubel, F. M., R. Brent, R. E. Kingston, D. D. Moore, J. G. Seidman, J. A. Smith, and K. Struhl. 1992. Current protocols in molecular biology. Greene Publishing Associates and Wiley Interscience, New York, N.Y.
-
- Beal, R., and W. B. Betts. 2000. Role of rhamnolipid biosurfactants in the uptake and mineralization of hexadecane in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 89:158-168. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

