Hippocampal CA1 circuitry dynamically gates direct cortical inputs preferentially at theta frequencies
- PMID: 16237162
- PMCID: PMC2048747
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2992-05.2005
Hippocampal CA1 circuitry dynamically gates direct cortical inputs preferentially at theta frequencies
Abstract
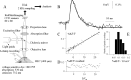
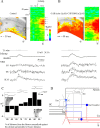
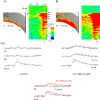
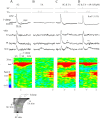
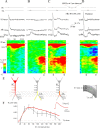
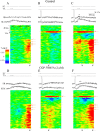
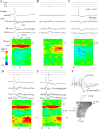
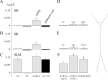
Hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons receive intrahippocampal and extrahipppocampal inputs during theta cycle, whose relative timing and magnitude regulate the probability of CA1 pyramidal cell spiking. Extrahippocampal inputs, giving rise to the primary theta dipole in CA1 stratum lacunosum moleculare, are conveyed by the temporoammonic pathway. The temporoammonic pathway impinging onto the CA1 distal apical dendritic tuft is the most electrotonically distant from the perisomatic region yet is critical in regulating CA1 place cell activity during theta cycles. How does local hippocampal circuitry regulate the integration of this essential, but electrotonically distant, input within the theta period? Using whole-cell somatic recording and voltage-sensitive dye imaging with simultaneous dendritic recording of CA1 pyramidal cell responses, we demonstrate that temporoammonic EPSPs are normally compartmentalized to the apical dendritic tuft by feedforward inhibition. However, when this input is preceded at a one-half theta cycle interval by proximally targeted Schaffer collateral activity, temporoammonic EPSPs propagate to the soma through a joint, codependent mechanism involving activation of Schaffer-specific NMDA receptors and presynaptic inhibition of GABAergic terminals. These afferent interactions, tuned for synaptic inputs arriving one-half theta interval apart, are in turn modulated by feedback inhibition initiated via axon collaterals of pyramidal cells. Therefore, CA1 circuit integration of excitatory inputs endows the CA1 principal cell with a novel property: the ability to function as a temporally specific "AND" gate that provides for sequence-dependent readout of distal inputs.
Figures

References
-
- Blanton MG, LoTurco JJ, Kriegstein AR (1989) Whole cell recording from neurons in slices of reptilian and mammalian cerebral cortex. J Neurosci Methods 30: 203-210. - PubMed
-
- Blasco-Ibáñez JM, Freund TF (1995) Synaptic input of horizontal interneurons in stratum oriens of the hippocampal CA1 subfield: structural basis of feed-back activation. Eur J Neurosci 7: 2170-2180. - PubMed
-
- Brankack J, Stewart M, Fox SE (1993) Current source density analysis of the hippocampal theta rhythm: associated sustained potentials and candidate synaptic generators. Brain Res 615: 310-327. - PubMed
-
- Brun VH, Otnæss MK, Molden S, Steffenach HA, Witter MP, Moser MB, Moser EI (2002) Place cells and place recognition maintained by direct entorhinal-hippocampal circuitry. Science 296: 2243-2246. - PubMed
-
- Buzsáki G (2002) Theta oscillations in the hippocampus. Neuron 33: 325-340. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
