Fyn kinase induces synaptic and cognitive impairments in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 16237174
- PMCID: PMC6725734
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2980-05.2005
Fyn kinase induces synaptic and cognitive impairments in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
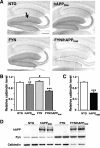
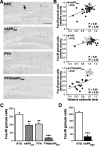
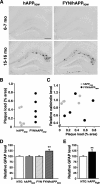
Human amyloid precursor protein (hAPP) transgenic mice with high levels of amyloid-beta (Abeta) develop behavioral deficits that correlate with the depletion of synaptic activity-related proteins in the dentate gyrus. The tyrosine kinase Fyn is altered in Alzheimer's disease brains and modulates premature mortality and synaptotoxicity in hAPP mice. To determine whether Fyn also modulates Abeta-induced behavioral deficits and depletions of synaptic activity-dependent proteins, we overexpressed Fyn in neurons of hAPP mice with moderate levels of Abeta production. Compared with nontransgenic controls and singly transgenic mice expressing hAPP or FYN alone, doubly transgenic FYN/hAPP mice had striking depletions of calbindin, Fos, and phosphorylated ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kinase), impaired neuronal induction of Arc, and impaired spatial memory retention. These deficits were qualitatively and quantitatively similar to those otherwise seen only in hAPP mice with higher Abeta levels. Surprisingly, levels of active Fyn were lower in high expresser hAPP mice than in NTG controls and lower in FYN/hAPP mice than in FYN mice. Suppression of Fyn activity may result from dephosphorylation by striatal-enriched phosphatase, which was upregulated in FYN/hAPP mice and in hAPP mice with high levels of Abeta. Thus, increased Fyn expression is sufficient to trigger prominent neuronal deficits in the context of even relatively moderate Abeta levels, and inhibition of Fyn activity may help counteract Abeta-induced impairments.
Figures






References
-
- Arancio O, Zhang HP, Chen X, Lin C, Trinchese F, Puzzo D, Liu S, Hegde A, Yan SF, Stern A, Luddy JS, Lue LF, Walker DG, Roher A, Buttini M, Mucke L, Li W, Schmidt AM, Kindy M, Hyslop PA, et al. (2004) RAGE potentiates Aβ-induced perturbation of neuronal function in transgenic mice. EMBO J 23: 4096-4105. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Atkins CM, Selcher JC, Petraitis JJ, Trzaskos JM, Sweatt JD (1998) The MAPK cascade is required for mammalian associative learning. Nat Neurosci 1: 602-609. - PubMed
-
- Bi X, Gall CM, Zhou J, Lynch G (2002) Uptake and pathogenic effects of amyloid beta peptide 1-42 are enhanced by integrin antagonists and blocked by NMDA receptor antagonists. Neuroscience 112: 827-840. - PubMed
-
- Chawla MK, Guzowski JF, Ramirez-Amaya V, Lipa P, Hoffman KL, Marriott LK, Worley PF, McNaughton BL, Barnes CA (2005) Sparse, environmentally selective expression of Arc RNA in the upper blade of the rodent fascia dentata by brief spatial experience. Hippocampus 15: 579-586. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
