Akt contributes to neuroprotection by hypothermia against cerebral ischemia in rats
- PMID: 16237183
- PMCID: PMC6725740
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3163-05.2005
Akt contributes to neuroprotection by hypothermia against cerebral ischemia in rats
Abstract
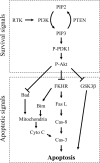
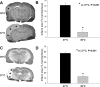
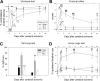
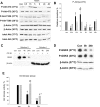
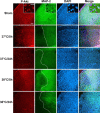
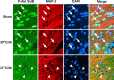
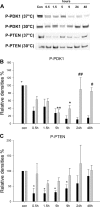
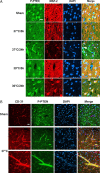
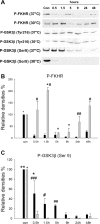
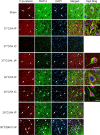
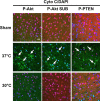
Activation of the Akt/protein kinase B (PKB) kinase pathway can be neuroprotective after stroke. Akt is activated by growth factors via a phosphorylation-dependent pathway involving the kinases phosphoinositide 3 (PI3) kinase and phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1) and is negatively regulated by phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN). Akt kinase blocks apoptosis by phosphorylating the substrates forkhead transcription factor (FKHR) and glycogen synthase kinase 3beta (GSK3beta). We found that intra-ischemic hypothermia (30 degrees C) reduced infarct size and improved functional outcomes up to 2 months. Changes in phosphorylation levels of Akt, as measured by Western blots and immunostaining, differed from levels of Akt activity measured in an in vitro assay in normothermic animals. Hypothermia blocked most of these changes and maintained Akt activity. Inhibition of PI3/Akt enlarged infarct size in hypothermic animals. Hypothermia improved phosphorylation of PDK1, PTEN, and FKHR. Hypothermia did not improve GSK3beta (Ser9) phosphorylation but blocked the nuclear translocation of phosphorylated beta-catenin (Ser33/37/Thr41) downstream of GSK3beta. Phosphorylation levels of PTEN, Akt, and Akt substrate decreased before apoptotic cytochrome c release and degradation of microtubule-associated protein-2, a marker of neuronal survival. Hypothermia may protect from ischemic damage in part by preserving Akt activity and attenuating the apoptotic effects of PTEN, PDK1, and FKHR.
Figures
References
-
- Abe T, Takagi N, Nakano M, Furuya M, Takeo S (2004) Altered Bad localization and interaction between Bad and Bcl-xL in the hippocampus after transient global ischemia. Brain Res 1009: 159-168. - PubMed
-
- Bederson JB, Pitts LH, Tsuji M, Nishimura MC, Davis RL, Bartkowski H (1986) Rat middle cerebral artery occlusion: evaluation of the model and development of a neurologic examination. Stroke 17: 472-476. - PubMed
-
- Bellacosa A, Chan TO, Ahmed NN, Datta K, Malstrom S, Stokoe D, Mc-Cormick F, Feng J, Tsichlis P (1998) Akt activation by growth factors is a multiple-step process: the role of the PH domain. Oncogene 17: 313-325. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
