The Cardiff Anomalous Perceptions Scale (CAPS): a new validated measure of anomalous perceptual experience
- PMID: 16237200
- PMCID: PMC2632213
- DOI: 10.1093/schbul/sbj014
The Cardiff Anomalous Perceptions Scale (CAPS): a new validated measure of anomalous perceptual experience
Abstract
The study describes the Cardiff Anomalous Perceptions Scale (CAPS), a new validated measure of perceptual anomalies. The 32-item CAPS measure is a reliable, self-report scale, which uses neutral language, demonstrates high content validity, and includes subscales that measure distress, intrusiveness, and frequency of anomalous experience. The CAPS was completed by a general population sample of 336 participants and 20 psychotic inpatients. Approximately 11% of the general population sample scored above the mean of the psychotic patient sample, although, as a group, psychotic inpatients scored significantly more than the general population on all CAPS subscales. A principal components analysis of the general population data revealed 3 components: "clinical psychosis" (largely Schneiderian first-rank symptoms), "temporal lobe disturbance" (largely related to temporal lobe epilepsy and related seizure-like disturbances) and "chemosensation" (largely olfactory and gustatory experiences), suggesting that there are multiple contributory factors underlying anomalous perceptual experience and the "psychosis continuum."
Figures

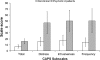
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association; 1994.
-
- Johns LC, van Os J. The continuity of psychotic experiences in the general population. Clin Psychol Rev. 2001;21:1125–1141. - PubMed
-
- van Os J. Is there a continuum of psychotic experiences in the general population? Epidemiol Psychiatr Soc. 2003;12:242–252. - PubMed
-
- Peters ER, Joseph S, Day S, Garety P. Measuring delusional ideation: the 21-item Peters et al. Delusions Inventory (PDI) Schizophr Bull. 2005;30:1005–1016. - PubMed
-
- Peters ER, Joseph SA, Garety PA. Measurement of delusional ideation in the normal population: introducing the PDI (Peters et al., Delusions Inventory) Schizophr Bull. 1999;25:553–576. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

