A multiplex polymerase chain reaction microarray assay to detect bioterror pathogens in blood
- PMID: 16237218
- PMCID: PMC1888491
- DOI: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60579-X
A multiplex polymerase chain reaction microarray assay to detect bioterror pathogens in blood
Abstract
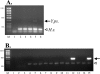
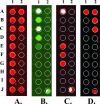
Heightened concern about the dangers of bioterrorism requires that measures be developed to ensure the safety of the blood supply. Multiplex detection of such agents using a blood-screening DNA microarray is a sensitive and specific method to screen simultaneously for a number of suspected agents. We have developed and optimized a multiplex polymerase chain reaction microarray assay to screen blood for three potential bioterror bacterial pathogens and a human ribosomal RNA gene internal control. The analytical sensitivity of the assay was demonstrated to be 50 colony-forming units/ml for Bacillus anthracis, Francisella tularensis, and Yersinia pseudotuberculosis (surrogate for Yersinia pestis). The absence of any false-positives demonstrated high analytical specificity. Screening B. anthracis-infected mouse blood samples and uninfected controls demonstrated effectiveness and specificity in a preclinical application. This study represents proof of the concept of microarray technology to screen simultaneously for multiple bioterror pathogens in blood samples.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Development of a multiplex PCR-suspension array for simultaneous detection of five bioterrorism bacteria].Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009 Mar;40(2):325-9. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2009. PMID: 19462919 Chinese.
-
Discrimination between biothreat agents and 'near neighbor' species using a resequencing array.FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008 Dec;54(3):356-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-695X.2008.00486.x. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2008. PMID: 19049648
-
A novel semiquantitative fluorescence-based multiplex polymerase chain reaction assay for rapid simultaneous detection of bacterial and parasitic pathogens from blood.J Mol Diagn. 2005 May;7(2):268-75. doi: 10.1016/S1525-1578(10)60554-5. J Mol Diagn. 2005. PMID: 15858151 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Anthrax Detection: Overview of Bioprobes and Biosensors.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2015 Jun;176(4):957-77. doi: 10.1007/s12010-015-1625-z. Epub 2015 May 19. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2015. PMID: 25987133 Review.
-
Detection technologies for Bacillus anthracis: prospects and challenges.J Microbiol Methods. 2010 Jul;82(1):1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2010.04.005. Epub 2010 Apr 22. J Microbiol Methods. 2010. PMID: 20399814 Review.
Cited by
-
Customizable PCR-microplate array for differential identification of multiple pathogens.J Food Prot. 2013 Nov;76(11):1948-57. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-13-153. J Food Prot. 2013. PMID: 24215700 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplex detection and identification of viral, bacterial, and protozoan pathogens in human blood and plasma using an expanded high-density resequencing microarray platform.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Jun 20;11:1419213. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1419213. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38966129 Free PMC article.
-
[Microbiological diagnosis: Etiologic driven and syndrome driven].Antibiotiques (Paris). 2009 Feb;11(1):37-48. doi: 10.1016/j.antib.2008.10.002. Epub 2008 Nov 29. Antibiotiques (Paris). 2009. PMID: 32288524 Free PMC article. French.
-
Rapid focused sequencing: a multiplexed assay for simultaneous detection and strain typing of Bacillus anthracis, Francisella tularensis, and Yersinia pestis.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56093. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056093. Epub 2013 Feb 13. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23418519 Free PMC article.
-
Reverse line blot macroarray for simultaneous detection and characterization of four biological warfare agents.Indian J Microbiol. 2013 Mar;53(1):41-7. doi: 10.1007/s12088-012-0330-7. Epub 2012 Nov 6. Indian J Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 24426077 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

