Two transactivation mechanisms cooperate for the bulk of HIF-1-responsive gene expression
- PMID: 16237459
- PMCID: PMC1283945
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7600846
Two transactivation mechanisms cooperate for the bulk of HIF-1-responsive gene expression
Abstract
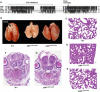
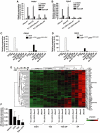
The C-terminal activation domain (C-TAD) of the hypoxia-inducible transcription factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha binds the CH1 domains of the related transcriptional coactivators CREB-binding protein (CBP) and p300, an oxygen-regulated interaction thought to be highly essential for hypoxia-responsive transcription. The role of the CH1 domain in vivo is unknown, however. We created mutant mice bearing deletions in the CH1 domains (DeltaCH1) of CBP and p300 that abrogate their interactions with the C-TAD, revealing that the CH1 domains of CBP and p300 are genetically non-redundant and indispensable for C-TAD transactivation function. Surprisingly, the CH1 domain was only required for an average of approximately 35-50% of global HIF-1-responsive gene expression, whereas another HIF transactivation mechanism that is sensitive to the histone deacetylase inhibitor trichostatin A (TSA(S)) accounts for approximately 70%. Both pathways are required for greater than 90% of the response for some target genes. Our findings suggest that a novel functional interaction between the protein acetylases CBP and p300, and deacetylases, is essential for nearly all HIF-responsive transcription.
Figures



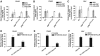
References
-
- Alarcon JM, Malleret G, Touzani K, Vronskaya S, Ishii S, Kandel ER, Barco A (2004) Chromatin acetylation, memory, and LTP are impaired in CBP(+/−) mice; a model for the cognitive deficit in Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome and its amelioration. Neuron 42: 947–959 - PubMed
-
- Brugarolas JB, Vazquez F, Reddy A, Sellers WR, Kaelin WG Jr (2003) TSC2 regulates VEGF through mTOR-dependent and -independent pathways. Cancer Cell 4: 147–158 - PubMed
-
- Bruick RK (2003) Oxygen sensing in the hypoxic response pathway: regulation of the hypoxia-inducible transcription factor. Genes Dev 17: 2614–2623 - PubMed
-
- Compernolle V, Brusselmans K, Acker T, Hoet P, Tjwa M, Beck H, Plaisance S, Dor Y, Keshet E, Lupu F, Nemery B, Dewerchin M, Van Veldhoven P, Plate K, Moons L, Collen D, Carmeliet P (2002) Loss of HIF-2alpha and inhibition of VEGF impair fetal lung maturation, whereas treatment with VEGF prevents fatal respiratory distress in premature mice. Nat Med 8: 702–710 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

