Lysophosphatidic acid transactivates both c-Met and epidermal growth factor receptor, and induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human colon cancer LoVo cells
- PMID: 16237757
- PMCID: PMC4481480
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i36.5638
Lysophosphatidic acid transactivates both c-Met and epidermal growth factor receptor, and induces cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human colon cancer LoVo cells
Abstract
Aim: To examine whether lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) induces phosphorylation of c-Met and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), both of which have been proposed as prognostic markers of colorectal cancer, and whether LPA induces cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in human colon cancer cells.
Methods: Using a human colon cancer cell line, LoVo cells, we performed immunoprecipitation analysis, followed by Western blot analysis. We also examined whether LPA induced COX-2 expression, by Western blot analysis.
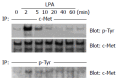
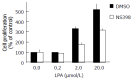
Results: Immunoprecipitation analysis revealed that 10 micromol/L LPA induced tyrosine phosphorylation of c-Met and EGFR in LoVo cells within a few minutes. We found that c-Met tyrosine phosphorylation induced by LPA was not attenuated by pertussis toxin or a matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor, in marked contrast to the results for EGFR. In addition, 0.2-40 micromol/L LPA induced COX-2 expression in a dose-dependent manner.
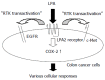
Conclusion: Our results suggest that LPA acts upstream of various receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) and COX-2, and thus may act as a potent stimulator of colorectal cancer.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TNF-α and LPA promote synergistic expression of COX-2 in human colonic myofibroblasts: role of LPA-mediated transactivation of upregulated EGFR.BMC Gastroenterol. 2013 May 20;13:90. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-13-90. BMC Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23688423 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophosphatidic acid-induced effects in human colon carcinoma DLD1 cells are partially dependent on transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor.J Surg Res. 2006 May;132(1):56-61. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2005.07.040. Epub 2005 Nov 14. J Surg Res. 2006. PMID: 16289596
-
Lysophosphatidic acid-induced transactivation of epidermal growth factor receptor regulates cyclo-oxygenase-2 expression and prostaglandin E(2) release via C/EBPbeta in human bronchial epithelial cells.Biochem J. 2008 May 15;412(1):153-62. doi: 10.1042/BJ20071649. Biochem J. 2008. PMID: 18294142 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophosphatidic acid upregulates vascular endothelial growth factor-C and tube formation in human endothelial cells through LPA(1/3), COX-2, and NF-kappaB activation- and EGFR transactivation-dependent mechanisms.Cell Signal. 2008 Oct;20(10):1804-14. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.06.008. Epub 2008 Jun 21. Cell Signal. 2008. PMID: 18627789
-
Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 2 and Gi/Src pathway mediate cell motility through cyclooxygenase 2 expression in CAOV-3 ovarian cancer cells.Exp Mol Med. 2008 Dec 31;40(6):607-16. doi: 10.3858/emm.2008.40.6.607. Exp Mol Med. 2008. PMID: 19116446 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Thrombocytosis before pre-operative chemoradiotherapy predicts poor response and shorter local recurrence-free survival in rectal cancer.Int J Colorectal Dis. 2013 Apr;28(4):527-35. doi: 10.1007/s00384-012-1594-4. Epub 2012 Oct 19. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2013. PMID: 23080345
-
Deregulation of lysophosphatidic acid metabolism in oral cancer promotes cell migration via the up-regulation of COX-2.PeerJ. 2020 Nov 11;8:e10328. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10328. eCollection 2020. PeerJ. 2020. PMID: 33240646 Free PMC article.
-
Lysophosphatidic acid signaling in airway epithelium: role in airway inflammation and remodeling.Cell Signal. 2009 Mar;21(3):367-77. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2008.10.010. Epub 2008 Oct 26. Cell Signal. 2009. PMID: 18996473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates gastric cancer cell proliferation via ERK1-dependent upregulation of sphingosine kinase 1 transcription.FEBS Lett. 2010 Sep 24;584(18):4077-82. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2010.08.035. Epub 2010 Sep 7. FEBS Lett. 2010. PMID: 20804754 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine kinase 1 is upregulated with lysophosphatidic acid receptor 2 in human colorectal cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Feb 28;22(8):2503-11. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i8.2503. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26937138 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yiu HY, Whittemore AS, Shibata A. Increasing colorectal cancer incidence rates in Japan. Int J Cancer. 2004;109:777–781. - PubMed
-
- Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S, Holmgren E, et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2335–2342. - PubMed
-
- Saltz LB, Meropol NJ, Loehrer PJ, Needle MN, Kopit J, Mayer RJ. Phase II trial of cetuximab in patients with refractory colorectal cancer that expresses the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Clin Oncol. 2004;22:1201–1208. - PubMed
-
- Cunningham D, Humblet Y, Siena S, Khayat D, Bleiberg H, Santoro A, Bets D, Mueser M, Harstrick A, Verslype C, et al. Cetuximab monotherapy and cetuximab plus irinotecan in irinotecan-refractory metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004;351:337–345. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

