Pivotal role of Harakiri in the induction and prevention of gentamicin-induced hearing loss
- PMID: 16239342
- PMCID: PMC1276101
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0508053102
Pivotal role of Harakiri in the induction and prevention of gentamicin-induced hearing loss
Abstract
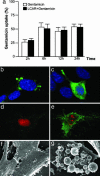
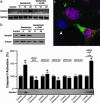
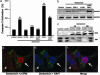
Gentamicin is a widely used ototoxic agent. In this study, we shed light on the mechanisms underlying gentamicin-induced hearing loss. More importantly, we demonstrate in vivo and in vitro the effectiveness of a strategy for preventing drug-induced hearing loss using l-carnitine (LCAR), a safe micronutrient that plays a key role in energy metabolism and detoxification [Rebouche, C. J. & Seim, H. (1998) Annu. Rev. Nutr. 18, 39-61]. We show that LCAR prevents changes in hearing threshold and cochlear damage in newborn guinea pigs exposed to gentamicin in utero. Mechanistically, gentamicin-induced apoptosis of auditory cells is mediated by the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) 1/2 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway through up-regulation of the proapoptotic factor Harakiri (Hrk). Most important, small interfering RNA (siRNA) experiments demonstrate that Hrk up-regulation is crucial for gentamicin-induced apoptosis. LCAR, in contrast, prevents both gentamicin-induced Hrk up-regulation and apoptosis acting by means of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK). Together, these results outline pathways for gentamicin-induced hearing loss and its prevention and assign a key role to Hrk in these processes. Thus, our data offer a conceptual framework for designing clinical trials using a safe micronutrient, LCAR, as a simple preventive strategy for iatrogenically induced ototoxicity.
Figures

References
-
- Chambers, H. F. & Sande, M. A. (1996) in Goodman & Gilman's The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics, eds. Hardman, J. G., Limbird, L. E., Molinoff, P. B., Ruddon, R. W. & Gilman, A. G. (McGraw-Hill, New York), pp. 1103-1121.
-
- Romero, R., Espinoza, J., Chaiworapongsa, T. & Kalache, K. (2002) Semin. Neonatol. 7, 259-274. - PubMed
-
- Henley, C. M. & Rybak, L. P. (1995) Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 20, 68-90. - PubMed
-
- Priuska, E. M. & Schacht, J. (1995) Biochem. Pharmacol. 50, 1749-1752. - PubMed
-
- Forge, A. & Schacht, J. (2000) Audiol. Neurootol. 5, 3-22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

