Peptidoglycan recognition protein 2 (N-acetylmuramoyl-L-Ala amidase) is induced in keratinocytes by bacteria through the p38 kinase pathway
- PMID: 16239516
- PMCID: PMC1273900
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.11.7216-7225.2005
Peptidoglycan recognition protein 2 (N-acetylmuramoyl-L-Ala amidase) is induced in keratinocytes by bacteria through the p38 kinase pathway
Abstract
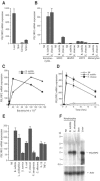
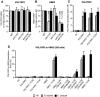
Human peptidoglycan recognition protein 2 (PGLYRP2) is an N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase that hydrolyzes bacterial peptidoglycan and is constitutively produced in the liver and secreted into the blood. Here we demonstrate that PGLYRP2 was not expressed in healthy human skin and had low expression in the eye. However, upon exposure to gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria or cytokines, PGLYRP2 expression was highly induced in keratinocytes and to a lower level in corneal epithelial cells. Expression of PGLYRP2 was not induced in nonepithelial cells. Exposure of keratinocytes to bacteria induced keratinocyte differentiation and stress response and inhibited activation of signal transduction molecules involved in cell proliferation. Induction of PGLYRP2 expression correlated with expression of differentiation markers (cytokeratins and transglutaminase). Bacteria induced activation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in keratinocytes, which was required for the induction of PGLYRP2 expression, because induction of PGLYRP2 transcription by bacteria was inhibited by SB203580 (a specific inhibitor of p38 MAPK) and by a dominant-negative p38 construct. Induction of PGLYRP2 expression by bacteria (in contrast to expression of human beta-defensin-2) was not mediated by Toll-like receptor 2 or 4. PGLYRP2 may function in the skin and the eyes as an inducible scavenger of proinflammatory peptidoglycan.
Figures

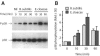
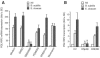
References
-
- Chamaillard, M., M. Hashimoto, Y. Horie, J. Masumoto, S. Qiu, L. Saab, Y. Ogura, A. Kawasaki, K. Fukase, S. Kusumoto, M. A. Valvano, S. J. Foster, T. W. Mak, G. Nunez, and N. Inohara. 2003. An essential role for NOD1 in host recognition of bacterial peptidoglycan containing diaminopimelic acid. Nat. Immunol. 7:702-707. - PubMed
-
- Chipman, D. M., and N. Sharon. 1967. Mechanism of lysozyme action. Science 165:454-464. - PubMed
-
- Dashti, S. R., T. Efimova, and R. L. Eckert. 2001. MEK7-dependent activation of p38 MAP kinase in keratinocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 276:8059-8063. - PubMed
-
- De Pauw, P., C. Neyt, E. Vanderwinkel, R. Wattiez, and P. Falmagne. 1995. Characterization of human serum N-acetylmuramyl-l-alanine amidase purified by affinity chromatography. Protein Expr. Purif. 6:371-378. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

