Studies of fibronectin-binding proteins of Streptococcus equi
- PMID: 16239519
- PMCID: PMC1273847
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.11.7243-7251.2005
Studies of fibronectin-binding proteins of Streptococcus equi
Abstract
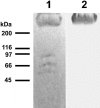
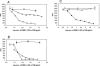
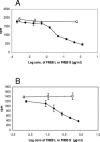
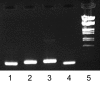
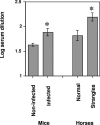
Streptococcus equi subsp. equi is the causative agent of strangles, a disease of the upper respiratory tract in horses. The initiation of S. equi subsp. equi infection is likely to involve cell surface-anchored molecules mediating bacterial adhesion to the epithelium of the host. The present study describes the cloning and characterization of FNEB, a fibronectin-binding protein with cell wall-anchoring motifs. FNEB can thus be predicted as cell surface located, contrary to the two previously characterized fibronectin-binding proteins in S. equi subsp. equi, FNE and SFS. Assays of antibody titers in horses and in experimentally infected mice indicate that the protein is immunogenic and expressed in vivo during S. equi subsp. equi infection. Using Western ligand blotting, it was shown that FNEB binds to the N-terminal 29-kDa fragment of fibronectin, while SFS and FNE both bind to the adjacent 40-kDa fragment. S. equi subsp. equi is known to bind fibronectin to a much lower degree than the closely related S. equi subsp. zooepidemicus, but the binding is primarily directed to the 29-kDa fragment. Inhibition studies using S. equi subsp. equi cells indicate that FNEB mediates cellular binding to fibronectin in this species.
Figures


References
-
- Anzai, T., J. F. Timoney, Y. Kuwamoto, Y. Fujita, R. Wada, and T. Inoue. 1999. In vivo pathogenicity and resistance to phagocytosis of Streptococcus equi strains with different levels of capsule expression. Vet. Microbiol. 67:277-286. - PubMed
-
- Artiushin, S. C., J. F. Timoney, A. S. Sheoran, and S. K. Muthupalani. 2002. Characterization and immunogenicity of pyrogenic mitogens SePE-H and SePE-I of Streptococcus equi. Microb. Pathog. 32:71-85. - PubMed
-
- Fernandez, E., V. Blume, P. Garrido, M. D. Collins, A. Mateos, L. Dominguez, and J. F. Fernandez-Garayzabal. 2004. Streptococcus equi subsp. ruminatorum subsp. nov., isolated from mastitis in small ruminants. Int J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 54:2291-2296. - PubMed
-
- Flanagan, J., N. Collin, J. Timoney, T. Mitchell, J. A. Mumford, and N. Chanter. 1998. Characterization of the haemolytic activity of Streptococcus equi. Microb. Pathog. 24:211-221. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

