CD28 is required for optimal induction, but not maintenance, of vaccine-induced immunity to Blastomyces dermatitidis
- PMID: 16239544
- PMCID: PMC1273838
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.11.7436-7441.2005
CD28 is required for optimal induction, but not maintenance, of vaccine-induced immunity to Blastomyces dermatitidis
Abstract
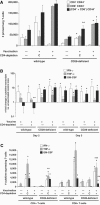
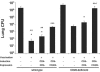
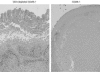
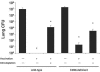
Cellular immunity mediated by T lymphocytes, in particular CD4+ and CD8+ type 1 cells, is the main defense against pathogenic fungi. Here, CD28-deficient (CD28-/-) mice were used to study the role of costimulation for the generation and maintenance of T-cell-mediated, type 1 cytokine-dependent mechanisms of vaccine immunity to Blastomyces dermatitidis infection. Disruption of CD28 costimulation reduced the number of type 1 CD4 and CD8 cells generated and impaired resistance to infection. Type 1 T-cell subsets generated in vaccinated CD28-/- mice were durable and protected mice for at least 3 months after vaccination. Our findings suggest that CD28 is required for the induction of optimal, protective T-cell responses to B. dermatitidis infection but may be dispensable for the maintenance of T-cell memory.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-12 is required for induction but not maintenance of protective, memory responses to Blastomyces dermatitidis: implications for vaccine development in immune-deficient hosts.J Immunol. 2005 Oct 15;175(8):5288-97. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.175.8.5288. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 16210634
-
Vaccine immunity to pathogenic fungi overcomes the requirement for CD4 help in exogenous antigen presentation to CD8+ T cells: implications for vaccine development in immune-deficient hosts.J Exp Med. 2003 Jun 2;197(11):1405-16. doi: 10.1084/jem.20030109. J Exp Med. 2003. PMID: 12782709 Free PMC article.
-
Requisite elements in vaccine immunity to Blastomyces dermatitidis: plasticity uncovers vaccine potential in immune-deficient hosts.J Immunol. 2002 Dec 15;169(12):6969-76. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.12.6969. J Immunol. 2002. PMID: 12471131
-
Progress in vaccination for histoplasmosis and blastomycosis: coping with cellular immunity.Med Mycol. 2005 Aug;43(5):381-9. doi: 10.1080/13693780500245875. Med Mycol. 2005. PMID: 16178365 Review.
-
Molecular basis of pathogenicity in Blastomyces dermatitidis: the importance of adhesion.Curr Opin Microbiol. 2000 Aug;3(4):339-43. doi: 10.1016/s1369-5274(00)00100-4. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10972490 Review.
Cited by
-
CD28 exerts protective and detrimental effects in a pulmonary model of paracoccidioidomycosis.Infect Immun. 2010 Nov;78(11):4922-35. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00297-10. Epub 2010 Aug 16. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20713624 Free PMC article.
-
Patterns of Expression of Vaginal T-Cell Activation Markers during Estrogen-Maintained Vaginal Candidiasis.Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2008 Dec 15;4(4):157-63. doi: 10.1186/1710-1492-4-4-157. Epub 2008 Dec 15. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol. 2008. PMID: 20525139 Free PMC article.
-
Inducible deletion of CD28 prior to secondary nippostrongylus brasiliensis infection impairs worm expulsion and recall of protective memory CD4⁺ T cell responses.PLoS Pathog. 2014 Feb 6;10(2):e1003906. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003906. eCollection 2014 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2014. PMID: 24516382 Free PMC article.
-
T cell responses to control fungal infection in an immunological memory lens.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 13;13:905867. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.905867. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36177012 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple immune factors are involved in controlling acute and chronic chikungunya virus infection.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014 Dec 4;8(12):e3354. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003354. eCollection 2014 Dec. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2014. PMID: 25474568 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bachmann, M. F., R. M. Zinkernagel, and A. Oxenius. 1998. Immune responses in the absence of costimulation: viruses know the trick. J. Immunol. 161:5791-5794. - PubMed
-
- Bertram, E. M., W. Dawicki, and T. H. Watts. 2004. Role of T-cell costimulation in antiviral immunity. Semin. Immunol. 16:185-196. - PubMed
-
- Bertram, E. M., P. Lau, and T. H. Watts. 2002. Temporal segregation of 4-1BB versus CD28-mediated costimulation: 4-1BB ligand influences T-cell numbers late in the primary response and regulates the size of the T-cell memory response following influenza infection. J. Immunol. 168:3777-3785. - PubMed
-
- Boussiotis, V. A., G. J. Freeman, J. G. Gribben, and L. M. Nadler. 1996. The role of B7-1/B7-2:CD28/CLTA-4 pathways in the prevention of anergy, induction of productive immunity and down-regulation of the immune response. Immunol. Rev. 153:5-26. - PubMed
-
- Boussiotis, V. A., J. G. Gribben, G. J. Freeman, and L. M. Nadler. 1994. Blockade of the CD28 costimulatory pathway: a means to induce tolerance. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 6:797-807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

