Decreased virulence of a gls24 mutant of Enterococcus faecalis OG1RF in an experimental endocarditis model
- PMID: 16239583
- PMCID: PMC1273851
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.73.11.7772-7774.2005
Decreased virulence of a gls24 mutant of Enterococcus faecalis OG1RF in an experimental endocarditis model
Abstract
In the current study, the gls24 disruption mutant TX10100, previously shown to be more sensitive to bile salts and attenuated in a mouse peritonitis model, showed an approximately fivefold higher 50% infective dose than wild-type OG1RF in a rat endocarditis model. When administered as a mixture, TX10100, unlike a downstream glsB mutant, was significantly outnumbered by OG1RF in vegetations, organs, and blood, despite being inoculated in greater numbers. These results indicate that gls24 is important in the pathogenesis of enterococcal endocarditis.
Figures
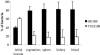
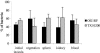
References
-
- Giard, J. C., A. Hartke, S. Flahaut, P. Boutibonnes, and Y. Auffray. 1997. Glucose starvation response in Enterococcus faecalis JH2-2: survival and protein analysis. Res. Microbiol. 148:27-35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

