P-glycoprotein deficiency at the blood-brain barrier increases amyloid-beta deposition in an Alzheimer disease mouse model
- PMID: 16239972
- PMCID: PMC1257538
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI25247
P-glycoprotein deficiency at the blood-brain barrier increases amyloid-beta deposition in an Alzheimer disease mouse model
Abstract
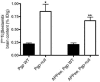
Accumulation of amyloid-beta (Abeta) within extracellular spaces of the brain is a hallmark of Alzheimer disease (AD). In sporadic, late-onset AD, there is little evidence for increased Abeta production, suggesting that decreased elimination from the brain may contribute to elevated levels of Abeta and plaque formation. Efflux transport of Abeta across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) contributes to Abeta removal from the brain. P-glycoprotein (Pgp) is highly expressed on the luminal surface of brain capillary endothelial cells and contributes to the BBB. In Pgp-null mice, we show that [I]Abeta40 and [I]Abeta42 microinjected into the CNS clear at half the rate that they do in WT mice. When amyloid precursor protein-transgenic (APP-transgenic) mice were administered a Pgp inhibitor, Abeta levels within the brain interstitial fluid significantly increased within hours of treatment. Furthermore, APP-transgenic, Pgp-null mice had increased levels of brain Abeta and enhanced Abeta deposition compared with APP-transgenic, Pgp WT mice. These data establish a direct link between Pgp and Abeta metabolism in vivo and suggest that Pgp activity at the BBB could affect risk for developing AD as well as provide a novel diagnostic and therapeutic target.
Figures
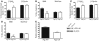
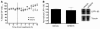

References
-
- DeMattos RB, Bales KR, Cummins DJ, Paul SM, Holtzman DM. Brain to plasma amyloid-beta efflux: a measure of brain amyloid burden in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Science. 2002;295:2264–2267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 CA094056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 NS034467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023084/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG023084/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG013956/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG023316/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS034467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS034467/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG23084/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AG013956/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R03 AG023316/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA94056/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- AI13956/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

