The burden of diarrhoea, shigellosis, and cholera in North Jakarta, Indonesia: findings from 24 months surveillance
- PMID: 16242013
- PMCID: PMC1276796
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2334-5-89
The burden of diarrhoea, shigellosis, and cholera in North Jakarta, Indonesia: findings from 24 months surveillance
Erratum in
- BMC Infect Dis. 2007;7:1
Abstract
Background: In preparation of vaccines trials to estimate protection against shigellosis and cholera we conducted a two-year community-based surveillance study in an impoverished area of North Jakarta which provided updated information on the disease burden in the area.
Methods: We conducted a two-year community-based surveillance study from August 2001 to July 2003 in an impoverished area of North Jakarta to assess the burden of diarrhoea, shigellosis, and cholera. At participating health care providers, a case report form was completed and stool sample collected from cases presenting with diarrhoea.
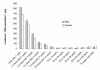
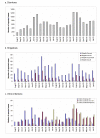
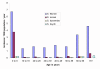
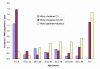
Results: Infants had the highest incidences of diarrhoea (759/1,000/year) and cholera (4/1,000/year). Diarrhea incidence was significantly higher in boys under 5 years (387/1,000/year) than girls under 5 years (309/1,000/year; p < 0.001). Children aged 1 to 2 years had the highest incidence of shigellosis (32/1,000/year). Shigella flexneri was the most common Shigella species isolated and 73% to 95% of these isolates were resistant to ampicillin, trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, chloramphenicol and tetracycline but remain susceptible to nalidixic acid, ciprofloxacin, and ceftriaxone. We found an overall incidence of cholera of 0.5/1,000/year. Cholera was most common in children, with the highest incidence at 4/1,000/year in those less than 1 year of age. Of the 154 V. cholerae O1 isolates, 89 (58%) were of the El Tor Ogawa serotype and 65 (42%) were El Tor Inaba. Thirty-four percent of patients with cholera were intravenously rehydrated and 22% required hospitalization. V. parahaemolyticus infections were detected sporadically but increased from July 2002 onwards.
Conclusion: Diarrhoea causes a heavy public health burden in Jakarta particularly in young children. The impact of shigellosis is exacerbated by the threat of antimicrobial resistance, whereas that of cholera is aggravated by its severe manifestations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Shigella-associated diarrhea in children in South Jakarta, Indonesia.Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2010 Mar;41(2):418-25. Southeast Asian J Trop Med Public Health. 2010. PMID: 20578526
-
A multicentre study of Shigella diarrhoea in six Asian countries: disease burden, clinical manifestations, and microbiology.PLoS Med. 2006 Sep;3(9):e353. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0030353. PLoS Med. 2006. PMID: 16968124 Free PMC article.
-
Occurrence of shigellosis in the young and elderly in rural China: results of a 12-month population-based surveillance study.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005 Aug;73(2):416-22. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2005. PMID: 16103614
-
Interventions for the control of diarrhoeal diseases among young children: chemoprophylaxis.Bull World Health Organ. 1985;63(2):295-315. Bull World Health Organ. 1985. PMID: 3893774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shigellosis remains an important problem in children less than 5 years of age in Thailand.Epidemiol Infect. 2005 Jun;133(3):469-74. doi: 10.1017/s0950268804003590. Epidemiol Infect. 2005. PMID: 15962553 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune responses to cholera in children.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2012 Apr;10(4):435-44. doi: 10.1586/eri.12.23. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2012. PMID: 22512753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Importance of cholera and other etiologies of acute diarrhea in post-earthquake Port-au-Prince, Haiti.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014 Mar;90(3):511-7. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.13-0514. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2014. PMID: 24445205 Free PMC article.
-
A changing picture of shigellosis in southern Vietnam: shifting species dominance, antimicrobial susceptibility and clinical presentation.BMC Infect Dis. 2009 Dec 15;9:204. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-9-204. BMC Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 20003464 Free PMC article.
-
Intimate partner violence and infant morbidity: evidence of an association from a population-based study in eastern Uganda in 2003.BMC Pediatr. 2007 Nov 7;7:34. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-7-34. BMC Pediatr. 2007. PMID: 17988374 Free PMC article.
-
Facilitated molecular typing of Shigella isolates using ERIC-PCR.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2012 Jun;86(6):1018-25. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2012.11-0671. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2012. PMID: 22665611 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

