Gastrin exerts pleiotropic effects on human melanoma cell biology
- PMID: 16242076
- PMCID: PMC1502029
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.05379
Gastrin exerts pleiotropic effects on human melanoma cell biology
Abstract
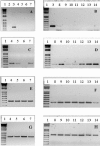
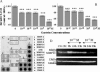
The effects of gastrin (G17) on the growth and migration factors of four human melanoma cell lines (HT-144, C32, G-361, and SKMEL-28) were investigated. The expression patterns of cholecystokinin (CCK)(A), CCK(B), and CCK(C) gastrin receptors were investigated in these cells and in seven clinical samples by means of reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Melanoma cells appear to express mRNA for CCK(C) receptors, but not for CCK(A) or CCK(B) receptors. Although gastrin does not significantly modify the growth characteristics of the cell lines under study, it significantly modifies their cell migration characteristics. These modifications occur at adhesion level by modifying the expression levels of alpha(v) and beta3 integrins, at motility level by modifying the organization of the actin cytoskeleton, and at invasion level by modifying the expression levels of matrix metalloproteinase 14. We recently demonstrated the presence of CCK(B) receptors in mouse endothelial cells involved in glioblastoma neoangiogenesis. Chronic in vivo administration of a selective CCK(B) receptor antagonist to mice bearing xenografts of human C32 melanoma cells significantly decreased levels of neoangiogenesis, resulting in considerable delays in the growth of these C32 xenografts. In conclusion, our study identifies the pleiotropic effects of gastrin on melanoma cell biology.
Figures



References
-
- Lawson DH. Update on the systemic treatment of malignant melanoma. Semin Oncol. 2004;31:33–37. - PubMed
-
- Kim KB, Eton O, East MJ, Hodges C, Papadopoulos NE, Grimm EA,, Bedikian AY. Pilot study of high-dose, concurrent biochemotherapy for advanced melanoma. Cancer. 2004;101:596–603. - PubMed
-
- Pollak MN, Schernhammer ES, Hankinson SE. Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004;4:505–518. - PubMed
-
- Satyamoorthy K, Li G, Vaidya B, Patel D, Herlyn M. Insulin-like growth factor-1 induces survival and growth of biologically early melanoma cells through both the mitogen-activated protein kinase and β-catenin pathways. Cancer Res. 2001;61:7318–7324. - PubMed
-
- Satyamoorthy K, Li G, Vaidya B, Kalabis J, Herlyn M. Insulin-like growth factor-1-induced migration of melanoma cells is mediated by interleukin-8 induction. Cell Growth Differ. 2002;13:87–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
