G protein betagamma11 complex translocation is induced by Gi, Gq and Gs coupling receptors and is regulated by the alpha subunit type
- PMID: 16242307
- PMCID: PMC2238718
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2005.09.007
G protein betagamma11 complex translocation is induced by Gi, Gq and Gs coupling receptors and is regulated by the alpha subunit type
Abstract
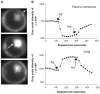
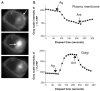
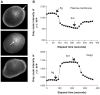
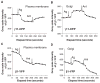
G protein activation by Gi/Go coupling M2 muscarinic receptors, Gq coupling M3 receptors and Gs coupling beta2 adrenergic receptors causes rapid reversible translocation of the G protein gamma11 subunit from the plasma membrane to the Golgi complex. Co-translocation of the beta1 subunit suggests that gamma11 translocates as a betagamma complex. Pertussis toxin ADP ribosylation of the alphai subunit type or substitution of the C terminal domain of alphao with the corresponding region of alphas inhibits gamma11 translocation demonstrating that alpha subunit interaction with a receptor and its activation are requirements for the translocation. The rate of gamma11 translocation is sensitive to the rate of activation of the G protein alpha subunit. alpha subunit types that show high receptor activated rates of guanine nucleotide exchange in vitro support high rates of gamma11 translocation compared to alpha subunit types that have a relatively lower rate of guanine nucleotide exchange. The results suggest that the receptor induced translocation of gamma11 is controlled by the rate of cycling of the G protein through active and inactive forms. They also demonstrate that imaging of gamma11 translocation can be used as a non-invasive tool to measure the relative activities of wild type or mutant receptor and alpha subunit types in a live cell.
Figures





References
-
- Akgoz M, Kalyanaraman V, Gautam N. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(49):51541. - PubMed
-
- Dell'Acqua ML, Carroll RC, Peralta EG. J Biol Chem. 1993;268(8):5676. - PubMed
-
- Hunt TW, Carroll RC, Peralta EG. J Biol Chem. 1994;269(47):29565. - PubMed
-
- Neves SR, Ram PT, Iyengar R. Science. 2002;296(5573):1636. - PubMed
-
- Wong SK. Neurosignals. 2003;12(1):1. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

