Role of Rac1 in Escherichia coli K1 invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells
- PMID: 16243562
- PMCID: PMC1525332
- DOI: 10.1016/j.micinf.2005.07.012
Role of Rac1 in Escherichia coli K1 invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells
Abstract
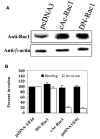
Escherichia coli K1 invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMEC) requires the reorganization of host cytoskeleton at the sites of bacterial entry. Both actin and myosin constitute the cytoskeletal architecture. We have previously shown that myosin light chain (MLC) phosphorylation by MLC kinase is regulated during E. coli invasion by an upstream kinase, p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1), which is an effector protein of Rac and Cdc42 GTPases, but not of RhoA. Here, we report that the binding of only Rac1 to PAK1 decreases in HBMEC upon infection with E. coli K1, which resulted in increased phosphorylation of MLC. Overexpression of a constitutively active (cAc) form of Rac1 in HBMEC blocked the E. coli invasion significantly, whereas overexpression of a dominant negative form had no effect. Increased PAK1 phosphorylation was observed in HBMEC expressing cAc-Rac1 with a concomitant reduction in the phosphorylation of MLC. Immunocytochemistry studies demonstrated that the inhibition of E. coli invasion into cAc-Rac1/HBMEC is due to lack of phospho-MLC recruitment to the sites of E. coli entry. Taken together the data suggest that E. coli modulates the binding of Rac1, but not Cdc42, to PAK1 during the invasion of HBMEC.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Modulation of myosin light-chain phosphorylation by p21-activated kinase 1 in Escherichia coli invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells.Infect Immun. 2003 May;71(5):2787-97. doi: 10.1128/IAI.71.5.2787-2797.2003. Infect Immun. 2003. PMID: 12704153 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 contributes to Escherichia coli K1 invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway.Infect Immun. 2010 Nov;78(11):4809-16. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00377-10. Epub 2010 Aug 30. Infect Immun. 2010. PMID: 20805333 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of focal adhesion kinase in Escherichia coli invasion of human brain microvascular endothelial cells.Infect Immun. 2000 Nov;68(11):6423-30. doi: 10.1128/IAI.68.11.6423-6430.2000. Infect Immun. 2000. PMID: 11035755 Free PMC article.
-
Invasion processes of pathogenic Escherichia coli.Int J Med Microbiol. 2005 Oct;295(6-7):463-70. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmm.2005.07.004. Int J Med Microbiol. 2005. PMID: 16238020 Review.
-
E. coli invasion of brain microvascular endothelial cells as a pathogenetic basis of meningitis.Subcell Biochem. 2000;33:47-59. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4757-4580-1_3. Subcell Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10804851 Review.
Cited by
-
p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) as a therapeutic target for cardiotoxicity.Arch Toxicol. 2022 Dec;96(12):3143-3162. doi: 10.1007/s00204-022-03384-1. Epub 2022 Sep 18. Arch Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36116095 Review.
-
The effects of cytotoxic necrotizing factor 1 expression in the uptake of Escherichia coli K1 by macrophages and the onset of meningitis in newborn mice.Virulence. 2016 Oct 2;7(7):806-18. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2016.1192730. Epub 2016 May 24. Virulence. 2016. PMID: 27221788 Free PMC article.
-
IQGAP1 mediates the disruption of adherens junctions to promote Escherichia coli K1 invasion of brain endothelial cells.Cell Microbiol. 2012 Sep;14(9):1415-33. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2012.01805.x. Epub 2012 May 24. Cell Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22519731 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of biopterin synthesis prevents Escherichia coli K1 invasion of brain endothelial cells and the development of meningitis in newborn mice.J Infect Dis. 2013 Jan 1;207(1):61-71. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jis656. Epub 2012 Oct 24. J Infect Dis. 2013. PMID: 23100563 Free PMC article.
-
Outer membrane protein A and OprF: versatile roles in Gram-negative bacterial infections.FEBS J. 2012 Mar;279(6):919-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2012.08482.x. Epub 2012 Feb 10. FEBS J. 2012. PMID: 22240162 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stoll BJ, Hansen N, Fanaroff AA, Wright LL, Carlo WA, Ehrenkranz RA, Lemons JA, Donovan EF, Stark AR, Tyson JE, Oh W, Bauer CR, Korones SB, Shankaran S, Laptook AR, Stevenson DK, Papile LA, Poole WK. Changes in pathogens causing early-onset sepsis in very-low-birth-weight infants. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:240–247. - PubMed
-
- Bokoch GM. Biology of the p21-activated kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 2003;72:743–781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

