Inhibitors of histone deacetylases target the Rb-E2F1 pathway for apoptosis induction through activation of proapoptotic protein Bim
- PMID: 16243973
- PMCID: PMC1276064
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0505585102
Inhibitors of histone deacetylases target the Rb-E2F1 pathway for apoptosis induction through activation of proapoptotic protein Bim
Abstract
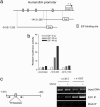
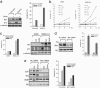
Inhibitors of histone deacetylases (HDACIs) are a new generation of anticancer agents that selectively kill tumor cells. However, the molecular basis for their tumor selectivity is not well understood. We investigated the effects of HDACIs on the oncogenic Rb-E2F1 pathway, which is frequently deregulated in human cancers. Here, we report that cancer cells with elevated E2F1 activity, caused either by enforced E2F1 expression, or by E1A oncogene expression, are highly susceptible to HDACI-induced cell death. This E2F1-mediated apoptosis is neither p53- nor p73-dependent but proceeds through selective induction of proapoptotic BH3-only protein Bim. We show that Bim is a direct target of E2F1 and that HDAC inhibition promotes the recruitment of E2F1 to the Bim promoter. Moreover, silencing of Bim by specific small interfering RNA (siRNA) effectively abolishes the E2F1-mediated cell death sensitization to HDACIs. These findings suggest that the oncogenic E2F1 pathway participates in HDACIs-induced apoptosis in cancer cells and underscore the importance of Bim as a key mediator of oncogene-induced apoptosis. Our study provides an important insight into the molecular mechanism of tumor selectivity of HDACIs and predicts that, clinically, HDACIs will be more effective in tumors with high E2F1 activity.
Figures
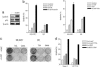
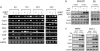

Similar articles
-
Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 is a direct target of E2F1 and contributes to histone deacetylase inhibitor-induced apoptosis through positive feedback regulation of E2F1 apoptotic activity.J Biol Chem. 2006 Apr 14;281(15):10508-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M512719200. Epub 2006 Feb 13. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16476732
-
Angiotensin II regulates activation of Bim via Rb/E2F1 during apoptosis: involvement of interaction between AMPKβ1/2 and Cdk4.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012 Aug 1;303(3):L228-38. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00087.2012. Epub 2012 Jun 1. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2012. PMID: 22659879 Free PMC article.
-
A combination of a ribonucleotide reductase inhibitor and histone deacetylase inhibitors downregulates EGFR and triggers BIM-dependent apoptosis in head and neck cancer.Oncotarget. 2012 Jan;3(1):31-43. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.430. Oncotarget. 2012. PMID: 22289787 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer cells' epigenetic composition and predisposition to histone deacetylase inhibitor sensitization.Epigenomics. 2011 Apr;3(2):145-55. doi: 10.2217/epi.11.12. Epigenomics. 2011. PMID: 21743813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To live or let die - complexity within the E2F1 pathway.Mol Cell Oncol. 2015 Jan 30;2(1):e970480. doi: 10.4161/23723548.2014.970480. eCollection 2015 Jan-Mar. Mol Cell Oncol. 2015. PMID: 27308406 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiotoxicity of molecularly targeted agents.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2011 Nov;7(4):221-33. doi: 10.2174/157340311799960636. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2011. PMID: 22758623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
α-Synuclein upregulates bim-mediated apoptosis by negatively regulating endogenous GCN5.Aging (Albany NY). 2022 Oct 27;14(20):8292-8301. doi: 10.18632/aging.204353. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Aging (Albany NY). 2022. PMID: 36309909 Free PMC article.
-
Impairment of organ-specific T cell negative selection by diabetes susceptibility genes: genomic analysis by mRNA profiling.Genome Biol. 2007;8(1):R12. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-1-r12. Genome Biol. 2007. PMID: 17239257 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR inhibitor AZD8055 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in laryngeal carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014 Feb 15;7(2):337-47. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 24600487 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous modulators and pharmacological inhibitors of histone deacetylases in cancer therapy.Oncogene. 2012 Feb 2;31(5):537-51. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.267. Epub 2011 Jul 4. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 21725353 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gabrielli, B. G., Johnstone, R. W. & Saunders, N. A. (2002) Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2, 337-353. - PubMed
-
- Johnstone, R. W. & Licht, J. D. (2003) Cancer Cell 4, 13-18. - PubMed
-
- Marks, P. A., Richon, V. M., Breslow, R. & Rifkind, R. A. (2001) Curr. Opin. Oncol. 13, 477-483. - PubMed
-
- Melnick, A. & Licht, J. D. (2002) Curr. Opin. Hematol. 9, 322-332. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

