The accuracy of ultrasound, stereotactic, and clinical core biopsies in the diagnosis of breast cancer, with an analysis of false-negative cases
- PMID: 16244544
- PMCID: PMC1409862
- DOI: 10.1097/01.sla.0000186186.05971.e0
The accuracy of ultrasound, stereotactic, and clinical core biopsies in the diagnosis of breast cancer, with an analysis of false-negative cases
Abstract
Objective: Preoperative core biopsy in breast cancer is becoming the standard of care. The aim of this study was to analyze the various methods of core biopsy with respect to diagnostic accuracy and to examine the management and outcome of those patients with false-negative biopsies.
Methods: All patients undergoing core biopsy for breast abnormalities over a 5-year period (1999-2003) were reviewed. The accuracy rates for each method of core biopsy, the histologic agreement between the core pathology and subsequent excision pathology, and the length of follow-up for cases of benign disease were studied. Patients whose biopsies were benign but who were subsequently diagnosed with cancer underwent detailed review.
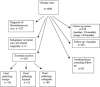
Results: There were 2427 core biopsies performed over the 5-year period, resulting in a final diagnosis of cancer in 1384 patients, benign disease in 954 patients, and atypical disease in 89 patients. Biopsy type consisted of 1279 ultrasound-guided cores, 739 clinically guided cores, and 409 stereotactic-guided cores. The overall false-negative rate was 6.1%, with specific rates for ultrasound-, clinical-, and stereotactic-guided cores of 1.7%, 13%, and 8.9%, respectively. False-negative biopsies occurred in 85 patients, and in 8 of these patients the diagnosis was delayed by greater than 2 months. In all other false-negative cases, "triple assessment" review allowed prompt recognition of discordant biopsy results and further evaluation.
Conclusion: Ultrasound guidance should be used to perform core biopsies in evaluating all breast abnormalities visible on ultrasound. Adherence to principles of triple assessment following biopsy allows for early recognition of the majority of false-negative cases.
Figures
References
-
- Farshid G, Rush G. The use of fine needle aspiration cytology and core biopsy in the assessment of highly suspicious mammographic calcifications: analysis of outcome for 182 lesions detected in the setting of population based breast cancer screening program. Cancer. 2003;99:357–364. - PubMed
-
- Dennison G, Anand R, Maker SH, et al. A prospective study of the use of fine needle aspiration cytology and core biopsy in the diagnosis of breast cancer. Breast J. 2003;9:491–493. - PubMed
-
- Westenend PJ, Sever AR, de Volder B, et al. A comparison of aspiration cytology and core needle biopsy in the evaluation of breast lesions. Cancer. 2001;93:146–150. - PubMed
-
- Verkooijen HM. Diagnostic accuracy of stereotactic large-core needle biopsy for nonpalpable breast disease: results of a multicenter prospective study with 95% surgical confirmation. Int J Cancer. 2002;99:853–859. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

