Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates epithelial-mesenchymal transformation in the proepicardium
- PMID: 16245329
- PMCID: PMC3160345
- DOI: 10.1002/dvdy.20593
Transforming growth factor-beta stimulates epithelial-mesenchymal transformation in the proepicardium
Abstract
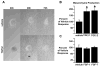
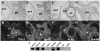
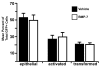
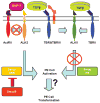
The proepicardium (PE) migrates over the heart and forms the epicardium. A subset of these PE-derived cells undergoes epithelial-mesenchymal transformation (EMT) and gives rise to cardiac fibroblasts and components of the coronary vasculature. We report that transforming growth factor-beta (TGFbeta) 1 and TGFbeta2 increase EMT in PE explants as measured by invasion into a collagen gel, loss of cytokeratin expression, and redistribution of ZO1. The type I TGFbeta receptors ALK2 and ALK5 are both expressed in the PE. However, only constitutively active (ca) ALK2 stimulates PE-derived epithelial cell activation, the first step in transformation, whereas caALK5 stimulates neither activation nor transformation in PE explants. Overexpression of Smad6, an inhibitor of ALK2 signaling, inhibits epithelial cell activation, whereas BMP7, a known ligand for ALK2, has no effect. These data demonstrate that TGFbeta stimulates transformation in the PE and suggest that ALK2 partially mediates this effect.
2005 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Transforming growth factor-beta induces loss of epithelial character and smooth muscle cell differentiation in epicardial cells.Dev Dyn. 2006 Jan;235(1):82-93. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.20629. Dev Dyn. 2006. PMID: 16258965
-
Activin receptor-like kinase 2 and Smad6 regulate epithelial-mesenchymal transformation during cardiac valve formation.Dev Biol. 2005 Apr 1;280(1):201-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2004.12.037. Dev Biol. 2005. PMID: 15766759
-
Signaling via the Tgf-beta type I receptor Alk5 in heart development.Dev Biol. 2008 Oct 1;322(1):208-18. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.07.038. Epub 2008 Aug 7. Dev Biol. 2008. PMID: 18718461 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple transforming growth factor-beta isoforms and receptors function during epithelial-mesenchymal cell transformation in the embryonic heart.Cells Tissues Organs. 2007;185(1-3):146-56. doi: 10.1159/000101315. Cells Tissues Organs. 2007. PMID: 17587820 Review.
-
Transforming growth factor-beta-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in the lens: a model for cataract formation.Cells Tissues Organs. 2005;179(1-2):43-55. doi: 10.1159/000084508. Cells Tissues Organs. 2005. PMID: 15942192 Review.
Cited by
-
Oxygen-Dependent Gene Expression in Development and Cancer: Lessons Learned from the Wilms' Tumor Gene, WT1.Front Mol Neurosci. 2011 Feb 24;4:4. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2011.00004. eCollection 2011. Front Mol Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21430823 Free PMC article.
-
Epicardium in Heart Development.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2020 Feb 3;12(2):a037192. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a037192. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2020. PMID: 31451510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human fetal and adult epicardial-derived cells: a novel model to study their activation.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016 Nov 29;7(1):174. doi: 10.1186/s13287-016-0434-9. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27899163 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-integrin αv therapy improves cardiac fibrosis after myocardial infarction by blunting cardiac PW1+ stromal cells.Sci Rep. 2020 Jul 9;10(1):11404. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-68223-8. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32647159 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient Differentiation of TBX18+/WT1+ Epicardial-Like Cells from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Using Small Molecular Compounds.Stem Cells Dev. 2017 Apr 1;26(7):528-540. doi: 10.1089/scd.2016.0208. Epub 2016 Nov 29. Stem Cells Dev. 2017. PMID: 27927069 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Attisano L, Wrana JL. Mads and Smads in TGF beta signalling. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1998;10:188–194. - PubMed
-
- Barnett JV, Desgrosellier JS. Early events in valvulogenesis: a signaling perspective. Birth Defects Res C Embryo Today. 2003;69:58–72. - PubMed
-
- Barnett JV, Moustakas A, Lin W, Wang XF, Lin HY, Galper JB, Maas RL. Cloning and developmental expression of the chick type II and type III TGF beta receptors. Dev Dyn. 1994;199:12–27. - PubMed
-
- Bassing CH, Howe DJ, Segarini PR, Donahoe PK, Wang XF. A single heteromeric receptor complex is sufficient to mediate biological effects of transforming growth factor-beta ligands. J Biol Chem. 1994a;269:14861–14864. - PubMed
-
- Bassing CH, Yingling JM, Howe DJ, Wang T, He WW, Gustafson ML, Shah P, Donahoe PK, Wang XF. A transforming growth factor beta type I receptor that signals to activate gene expression. Science. 1994b;263:87–89. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

